a practical guide to sap multi-bank connectivity book download is your ticket to mastering the art of seamless financial operations. Dive into a world where managing multiple bank relationships goes from a headache to a breeze, all with that laid-back, Bali-inspired vibe.
This guide unpacks the challenges businesses face, from manual reconciliation woes to the need for a centralized financial command center. We’re talking about smoothing out those payment processes and getting a crystal-clear view of your cash flow, making your financial operations as chill as a sunset surf.
Understanding the Need for SAP Multi-Bank Connectivity

In today’s intricate global financial landscape, businesses are increasingly navigating complex ecosystems involving multiple banking partners. This proliferation of relationships, while often a strategic necessity for optimized services and geographical reach, introduces significant operational friction. The inherent challenge lies in orchestrating a unified and efficient flow of financial data and transactional commands across these disparate banking entities, a task that, if mishandled, can lead to inefficiencies, increased costs, and diminished financial control.The management of financial operations, particularly those involving payments and bank statement reconciliation, has historically been a labor-intensive and error-prone endeavor.
Companies often find themselves grappling with the sheer volume and variety of bank formats, communication protocols, and reporting standards. This heterogeneity creates a substantial burden on treasury and finance departments, diverting valuable resources from strategic initiatives towards manual, repetitive tasks.
A centralized approach to bank communication offers a compelling paradigm shift, transforming the way financial operations are managed. By consolidating the interaction with multiple banking institutions into a single, cohesive platform, businesses can achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency, transparency, and control. This strategic integration streamlines workflows, reduces the potential for human error, and provides a holistic view of the company’s cash position and transactional activities.
Fundamental Challenges in Managing Multiple Bank Relationships, A practical guide to sap multi-bank connectivity book download
Businesses often encounter a spectrum of inherent difficulties when managing relationships with a diverse set of banking partners. These challenges stem from the very nature of decentralized financial interactions and can significantly impede operational agility and financial oversight.
- Disparate Communication Channels: Each bank typically operates with its own proprietary systems, file formats (e.g., MT940, CAMT.053 for statements, pain.001 for payments), and communication protocols (e.g., SFTP, SWIFTNet, APIs). Integrating with each of these individually is a complex and resource-intensive undertaking.
- Data Inconsistency and Format Translation: Receiving bank statements in various formats necessitates complex data mapping and transformation processes to align with internal accounting systems. Similarly, originating payment files requires adherence to each bank’s specific requirements.
- Lack of Real-time Visibility: Fragmented bank connectivity often results in delayed or incomplete visibility into cash balances and transaction statuses across different accounts and institutions, hindering effective cash management and forecasting.
- Increased Operational Risk: Manual processes for data entry, reconciliation, and payment initiation are inherently susceptible to human error, leading to potential financial losses, compliance breaches, and reputational damage.
- Higher Transaction Costs: Managing multiple bank interfaces, dealing with format conversions, and resolving reconciliation discrepancies manually contribute to elevated operational costs and can negate any benefits derived from diversified banking relationships.
Pain Points of Manual Bank Statement Reconciliation and Payment Execution
The reliance on manual processes for bank statement reconciliation and payment execution is a significant source of operational pain for finance departments. These pain points not only consume excessive time and resources but also introduce substantial risks.
- Time-Consuming Reconciliation: Manually matching thousands of transactions between bank statements and internal accounting records is an arduous and time-consuming process. This often leads to delays in closing periods and identifying discrepancies.
- Error-Prone Data Entry: Re-keying transaction data from bank statements into ERP systems or other financial tools is a breeding ground for errors. These inaccuracies can cascade through financial reports and impact decision-making.
- Delayed Payment Processing: Manually preparing and submitting payment files to different banks, often with varied formats and cut-off times, can lead to delays in critical payments, potentially incurring late fees or damaging supplier relationships.
- Lack of Audit Trail: Manual processes often lack a robust and easily accessible audit trail, making it difficult to track the lifecycle of a transaction or to provide evidence for internal or external audits.
- Inefficient Exception Handling: Identifying and resolving exceptions, such as mismatched transactions or returned payments, becomes a manual detective exercise, diverting valuable treasury resources.
Advantages of a Centralized Approach to Bank Communication
Adopting a centralized approach to bank communication, particularly through a dedicated multi-bank connectivity solution, fundamentally transforms financial operations by offering a suite of strategic advantages. This consolidated strategy moves away from the fragmented, ad-hoc methods of the past towards a more integrated and intelligent financial infrastructure.
- Streamlined Operations: A single point of integration simplifies the management of multiple banking relationships, reducing the complexity of IT infrastructure and maintenance.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Automation of statement retrieval, payment file generation, and reconciliation processes significantly reduces manual effort and accelerates financial closing cycles.
- Improved Visibility and Control: Real-time access to consolidated bank data provides a clear, up-to-the-minute view of cash positions across all accounts and banks, enabling better liquidity management and forecasting.
- Reduced Risk: Automation minimizes human error in data processing and payment execution, thereby mitigating financial and operational risks. Standardized, secure communication protocols also enhance data integrity.
- Cost Optimization: By reducing manual effort, minimizing errors, and potentially negotiating better banking terms due to consolidated volumes, a centralized approach leads to significant cost savings.
- Scalability and Agility: A robust solution can easily accommodate new banking relationships or changes in existing ones without requiring extensive IT development, allowing businesses to adapt quickly to evolving market conditions.
Core Business Objectives Addressed by Multi-Bank Connectivity
A well-implemented multi-bank connectivity solution is not merely a technical upgrade; it is a strategic enabler that directly supports critical business objectives across the finance and treasury functions. Its impact resonates from day-to-day operational efficiency to long-term financial resilience and strategic growth.
- Optimized Cash Management: By providing real-time, consolidated visibility into global cash positions, businesses can make more informed decisions regarding liquidity, optimize intercompany funding, and minimize idle cash balances. This directly contributes to improved working capital.
- Enhanced Payment Processing Efficiency: The ability to initiate and track payments across multiple banks from a single platform, with automated validation and reconciliation, ensures timely and accurate disbursement of funds, strengthening supplier relationships and avoiding late payment penalties.
- Improved Financial Reporting Accuracy: Automated data capture and reconciliation processes reduce the likelihood of errors in financial records, leading to more accurate and reliable financial statements and management reports.
- Strengthened Internal Controls and Compliance: A centralized system provides a clear audit trail for all financial transactions and communications, facilitating compliance with regulatory requirements and internal policies. Automated processes also reduce opportunities for fraud.
- Reduced Operational Costs: Automating manual tasks, eliminating redundant data entry, and minimizing reconciliation errors directly translate into lower operational expenses for the treasury and finance departments.
- Support for Global Expansion: As businesses expand into new markets, they often need to establish new banking relationships. A multi-bank connectivity solution simplifies the integration of these new banks, enabling smoother international operations.
Core Concepts of SAP Multi-Bank Connectivity

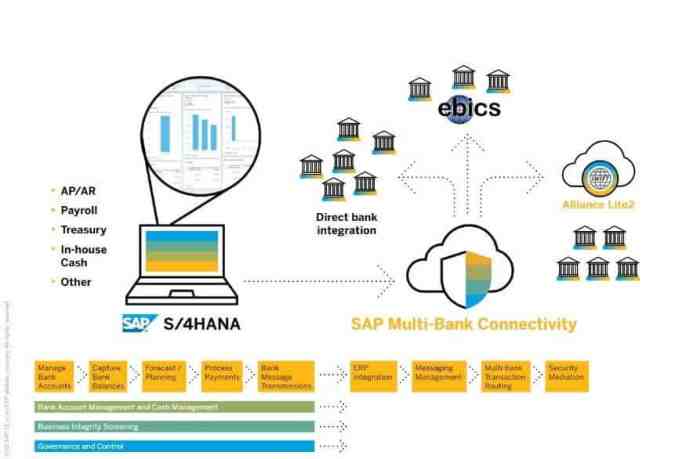
Understanding the foundational elements of SAP Multi-Bank Connectivity (MBC) is paramount for any organization aiming to streamline its financial operations and enhance its interaction with banking partners. MBC represents a significant evolution from traditional, often fragmented, approaches to bank communication, offering a centralized and standardized platform for managing financial transactions. This guide delves into the critical concepts that underpin MBC, providing a clear and actionable framework for its implementation and utilization.SAP MBC serves as a pivotal integration layer within the SAP financial ecosystem, acting as a bridge between a company’s SAP system and its various banking institutions.
Its primary role is to facilitate secure, efficient, and standardized communication for a wide array of financial processes, including payment initiation, status reporting, and cash management. By abstracting the complexities of individual bank interfaces, MBC allows businesses to focus on their core financial strategies rather than managing disparate connectivity solutions.
SAP Multi-Bank Connectivity Definition and Role
SAP Multi-Bank Connectivity (MBC) is a cloud-based solution designed to enable seamless and standardized communication between SAP applications and multiple banking partners. It acts as a central hub, abstracting the technical intricacies of individual bank communication channels and protocols. Within the SAP ecosystem, MBC plays a crucial role in modernizing treasury and finance operations by providing a unified platform for all bank interactions.
This consolidation not only simplifies IT landscapes but also enhances control and visibility over financial flows.
MBC is the strategic enabler for a truly digitalized treasury, fostering agility and efficiency in financial operations.
Key Components and Architecture of SAP MBC
The architecture of SAP MBC is designed for robustness, scalability, and security, comprising several key components that work in concert to facilitate interbank communication. At its core, MBC leverages SAP’s Business Technology Platform (BTP) to provide a secure and managed environment for these integrations.The primary components include:
- Connectivity Services: These services handle the secure establishment and management of connections to financial institutions. They abstract the underlying protocols and ensure data integrity during transmission.
- Data Transformation Engine: This component is responsible for converting financial data into standardized formats required by both SAP applications and banking partners, and vice versa. It ensures interoperability across different systems and formats.
- Monitoring and Alerting Tools: These provide real-time visibility into the status of all bank communications, enabling proactive identification and resolution of any issues. This includes tracking transaction statuses, connection health, and potential errors.
- Security Layer: Robust security measures, including encryption and authentication protocols, are embedded throughout the MBC architecture to protect sensitive financial data and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
The overall architecture is designed to be modular and extensible, allowing for the integration of new banks and services with relative ease. This flexibility is critical in a dynamic financial landscape where banking relationships and technological requirements can change rapidly.
Connection Types and Protocols Supported by SAP MBC
SAP MBC supports a diverse range of connection types and protocols to accommodate the varied requirements of financial institutions and regulatory mandates. This versatility ensures that organizations can connect with virtually any bank, regardless of their preferred communication methods.The primary connection types and protocols include:
- SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication): MBC offers robust support for SWIFTNet, a global network for secure financial messaging. This includes various SWIFT message types (e.g., MT101, MT940, MT942, CAMT.053, CAMT.054) crucial for payment initiation and account reporting. The integration with SWIFT ensures access to a vast network of financial institutions worldwide.
- File-Based Connectivity: This encompasses a broad category of connections where data is exchanged in structured files. Common formats include ISO 20022 XML, which is increasingly becoming the global standard, as well as legacy formats like CSV, TXT, and MT940/MT942 files. MBC facilitates the secure transmission and processing of these files via various transport protocols.
- APIs (Application Programming Interfaces): While file-based and SWIFT remain prevalent, MBC is increasingly supporting API-based integrations for real-time data exchange, particularly with fintech providers and newer banking platforms. These APIs offer more dynamic and immediate communication capabilities.
The choice of connection type and protocol often depends on the bank’s capabilities, the volume and type of transactions, and specific regional or industry standards. SAP MBC’s ability to support multiple options provides a significant advantage in managing complex banking relationships.
Standardized Communication Formats for Financial Transactions
A cornerstone of SAP MBC’s effectiveness lies in its ability to enforce and leverage standardized communication formats for financial transactions. This standardization is critical for reducing errors, improving processing efficiency, and ensuring compatibility across different systems and banks.The most prominent standardized format supported by SAP MBC is ISO 20022. This is a global, open, and rich standard for financial messaging, designed to address the needs of all market participants, including financial institutions, market infrastructures, and corporate customers.
It offers a comprehensive set of message definitions for various financial processes, moving beyond the limitations of older, proprietary formats.The benefits of using standardized formats like ISO 20022 within MBC include:
- Enhanced Data Richness: ISO 20022 messages can carry significantly more detailed information than traditional formats, enabling richer data for reconciliation, analytics, and reporting.
- Global Interoperability: A single standard simplifies communication across borders and between different financial systems, reducing the need for complex and costly custom mapping.
- Improved Automation: Standardized data structures facilitate greater automation in payment processing, cash management, and reconciliation, leading to reduced manual intervention and lower operational costs.
- Future-Proofing: As the financial industry continues to evolve, adopting a globally recognized standard like ISO 20022 ensures that an organization’s financial communication infrastructure remains relevant and adaptable.
SAP MBC acts as a crucial intermediary, transforming internal SAP data into these standardized formats for outgoing messages and vice versa for incoming messages. This capability ensures that organizations can communicate effectively with any bank that supports these common standards, irrespective of the specific implementation details.
Standardization in financial messaging, particularly with ISO 20022, is not merely a technical choice; it is a strategic imperative for achieving operational excellence and global financial agility.
Benefits of Implementing SAP Multi-Bank Connectivity
The integration of SAP Multi-Bank Connectivity (MBC) represents a significant leap forward for organizations grappling with the complexities of modern financial operations. Beyond mere connectivity, MBC fundamentally redefines how businesses interact with their banking partners, offering a robust framework for enhanced efficiency, accuracy, and strategic financial management. This section delves into the tangible advantages that accrue from adopting this advanced solution, demonstrating its transformative potential for financial departments.SAP MBC transcends the limitations of traditional point-to-point integrations, which are often cumbersome, costly, and prone to error.
By establishing a standardized, secure, and centralized communication channel with multiple banking institutions, MBC empowers organizations to streamline a multitude of financial processes. This consolidation not only simplifies operational workflows but also unlocks critical insights that drive better decision-making. The strategic imperative for implementing SAP MBC lies in its ability to address persistent challenges in payment processing, cash management, and regulatory adherence, thereby fostering a more agile and resilient financial ecosystem.
Streamlined Payment Processing
The most immediate and impactful benefit of SAP MBC is the radical simplification of payment processing. Gone are the days of disparate interfaces, manual data entry, and fragmented communication with various banks. MBC establishes a single, standardized channel for initiating and managing all outgoing payments, regardless of the banking partner. This not only accelerates the payment cycle but also significantly reduces the potential for errors.Consider a global enterprise with operations across several continents, each relying on different banking relationships.
Previously, processing payroll or supplier payments would involve generating payment files in specific formats for each bank, uploading them through individual bank portals, and manually reconciling confirmations. With SAP MBC, a single payment run in SAP can be configured to automatically generate and transmit payment instructions in the standardized ISO 20022 XML format to all designated banks. The system then automatically retrieves payment confirmations, status updates, and acknowledgments, consolidating this information directly within SAP.
This eliminates the need for manual file creation and transmission, drastically cutting down processing time and reducing the likelihood of duplicate payments or missed deadlines. For instance, a manufacturing company can now process international vendor payments within hours instead of days, avoiding late fees and maintaining stronger supplier relationships.
Improved Cash Visibility and Forecasting
The automation of bank statement retrieval is a cornerstone of enhanced cash visibility and forecasting enabled by SAP MBC. Manual reconciliation of bank statements is a time-consuming and error-prone task, often leading to outdated or incomplete cash positions. MBC automates the inbound flow of bank statements, providing real-time or near real-time access to financial data.Through the automated import of electronic bank statements (e.g., MT940, CAMT.053), SAP MBC ensures that the company’s cash ledger in SAP is consistently updated with actual bank balances and transaction details.
This immediate access to accurate data is crucial for effective cash management. For example, a retail chain can now monitor its daily cash inflows and outflows across all its bank accounts with unprecedented precision. This allows treasury teams to identify potential liquidity shortfalls or surpluses much earlier, enabling proactive measures such as optimizing short-term investments or arranging for necessary credit lines.
The improved accuracy and timeliness of this data also feed directly into more reliable cash flow forecasting models, allowing for better strategic financial planning and resource allocation.
Reduction in Manual Effort and Error Rates
The automation inherent in SAP MBC directly translates to a substantial reduction in manual effort within financial departments, consequently lowering associated error rates. Repetitive, data-intensive tasks that were once the domain of finance professionals are now handled by the system, freeing up valuable human capital for more strategic activities.Manual reconciliation of bank statements, for instance, often involves comparing hundreds or thousands of individual transactions between a bank statement and the general ledger.
This process is not only tedious but also highly susceptible to human error, such as transposed numbers or incorrect account assignments. SAP MBC automates a significant portion of this reconciliation process. By automatically matching incoming bank statement lines with open items in SAP, it drastically reduces the volume of manual exceptions that require investigation. This not only saves considerable time but also minimizes the financial impact of errors.
A study by a large utilities company indicated that after implementing SAP MBC, the time spent on bank reconciliation decreased by over 60%, and the number of reconciliation discrepancies requiring manual investigation dropped by 85%. This reduction in manual intervention leads to a more efficient and accurate financial closing process.
Enhanced Security and Compliance
In an era of increasing cyber threats and stringent regulatory demands, the security and compliance features of SAP MBC are paramount. The solution employs robust encryption protocols and secure communication channels to protect sensitive financial data during transmission and storage.SAP MBC utilizes industry-standard security measures, such as Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) and Transport Layer Security (TLS), to ensure that payment instructions and bank statements are transmitted securely between the company and its banking partners.
This significantly mitigates the risk of data interception or manipulation. Furthermore, the centralized nature of MBC provides a single point of control and audit trail for all bank interactions. This simplifies compliance with regulations such as the Payment Services Directive (PSD2) and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), as all financial transactions are logged and auditable within the SAP environment.
For example, a financial institution can leverage MBC to demonstrate adherence to strict anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) regulations by having a clear, documented history of all payment flows and communications with their banking partners. The ability to enforce standardized processes and maintain detailed audit logs significantly strengthens an organization’s overall compliance posture and reduces the risk of financial penalties.
Practical Steps for SAP Multi-Bank Connectivity Implementation

Transitioning from understanding the theoretical underpinnings of SAP Multi-Bank Connectivity (MBC) to its actual deployment requires a structured, methodical approach. This section demystifies the implementation process, offering a clear roadmap from initial project kickoff to ongoing operational excellence. It acknowledges that while the benefits are compelling, the journey to realizing them is paved with careful planning and execution.The successful integration of SAP MBC is not a monolithic task but rather a series of interconnected phases, each demanding specific attention and resources.
This guide breaks down these phases into actionable steps, providing the necessary detail to navigate the complexities of system requirements, configuration, and validation.
Initiating an SAP MBC Project
Launching an SAP MBC project effectively sets the stage for its ultimate success. This initial phase involves defining project scope, assembling the right team, and securing executive sponsorship. A clear understanding of business objectives and how MBC will address them is paramount.
- Define Project Objectives and Scope: Clearly articulate what the business aims to achieve with SAP MBC. This could include streamlining payment processes, enhancing real-time cash visibility, or automating reconciliation. Define which banking relationships and transaction types will be prioritized.
- Form a Dedicated Project Team: Assemble a cross-functional team comprising representatives from Finance, Treasury, IT, and potentially Procurement. Key roles include a Project Manager, SAP Functional Consultants (especially in Treasury and Finance modules), Technical Consultants for integration, and Business Process Owners.
- Secure Executive Sponsorship: Gain buy-in and active support from senior management. This ensures the project receives necessary resources, budget, and strategic alignment.
- Conduct a Feasibility Study and Business Case Development: Quantify the potential benefits (e.g., cost savings, efficiency gains) and estimate the implementation costs. This forms the basis of the business case for the project.
- Develop a Project Plan: Artikel the project timeline, key milestones, deliverables, and resource allocation. This plan should be realistic and account for potential risks.
Prerequisites for Setting Up SAP MBC
Before embarking on the configuration of SAP MBC, ensuring that the foundational elements are in place is critical. This involves a thorough assessment of your SAP landscape and the necessary authorizations to perform the required tasks. Neglecting these prerequisites can lead to significant delays and rework.A robust technical infrastructure and appropriate user permissions are non-negotiable for a smooth implementation. This section details the essential requirements that must be met.
System Requirements
SAP MBC leverages specific SAP technologies and requires a certain level of system capability. Ensuring these are met prevents technical roadblocks during implementation and operation.
- SAP S/4HANA or SAP ECC: SAP MBC is typically implemented on SAP S/4HANA, though compatibility with certain SAP ECC versions might exist for specific functionalities. The system must be on a supported release.
- SAP Cloud Platform Integration (CPI) or SAP NetWeaver Process Integration (PI/PO): A middleware solution is essential for connecting SAP systems to the SAP Bank Communication Management (BCM) or SAP S/4HANA Finance, and subsequently to the SAP Multi-Bank Connectivity service. SAP CPI is the strategic cloud-based solution.
- SAP Bank Communication Management (BCM): If not already in use, BCM needs to be implemented and configured within your SAP ERP system. It acts as the central hub for managing payment flows. For SAP S/4HANA, the functionalities are integrated within S/4HANA Finance.
- Network Connectivity: Secure and stable network connectivity between your SAP landscape and SAP’s cloud infrastructure is required. This often involves setting up secure tunnels or VPNs.
- Database Requirements: Ensure your database system can handle the increased data volume and processing demands associated with real-time transaction monitoring and reporting.
Authorizations
Proper user authorizations are crucial for both the implementation team and end-users to access and manage SAP MBC functionalities securely. Incorrect permissions can lead to unauthorized access or operational disruptions.
For those exploring a practical guide to SAP multi-bank connectivity book download, understanding bank operating hours is essential. It’s worth noting that to answer the question, are banks open weekends , you might find varying answers depending on the institution. Regardless, having the right resources, like a comprehensive SAP multi-bank connectivity book download, empowers efficient financial operations.
- SAP System Authorizations: Users responsible for configuring and managing SAP MBC within the SAP system (e.g., Finance, Treasury consultants) require specific roles and transaction codes related to BCM, payment processing, and system administration.
- SAP Cloud Platform Integration (CPI) Authorizations: Developers and administrators working on the integration flows in SAP CPI need appropriate authorizations to design, deploy, and monitor integration artifacts.
- Bank-Specific Access: While SAP MBC abstracts much of the direct bank interaction, there might be specific portals or interfaces provided by banks for initial setup, certificate exchange, or troubleshooting that require dedicated user accounts.
- Security Roles: Implement a role-based access control strategy to ensure that users only have access to the functionalities and data relevant to their roles, adhering to the principle of least privilege.
Configuring Bank Connections within SAP MBC
The core of SAP MBC lies in establishing and configuring secure connections to your various banking partners. This process is iterative and requires close collaboration with both your internal teams and the banks themselves. Precision in this phase is paramount for the reliable flow of financial data.This section Artikels the typical steps involved in setting up these critical connections, from initial communication to the final validation of data exchange.
Step-by-Step Configuration Process
- Initiate Communication with Banks: Contact your banking partners to inform them of your intention to use SAP MBC. Understand their specific requirements and supported communication protocols (e.g., SWIFTNet, SFTP, HTTPS).
- Obtain Bank Credentials and Certificates: Banks will provide necessary credentials, such as participant identifiers, and digital certificates required for secure communication. This is a critical security step.
- Configure SAP BCM/S/4HANA Finance Settings: Within your SAP system, configure the payment methods, house banks, and bank account details that will be used with MBC. This involves mapping internal SAP data to external bank communication requirements.
- Set up SAP Cloud Platform Integration (CPI) Flows: Design and develop the integration scenarios in SAP CPI. This involves creating interfaces to map data formats between SAP and the bank’s expected formats (e.g., ISO 20022 XML messages for payments, account statements).
- Establish Secure Network Connections: Configure secure communication channels between your SAP landscape, SAP CPI, and the banks. This may involve setting up VPNs, secure file transfer protocols (SFTP), or direct API connections.
- Configure Communication Parameters in SAP MBC: In the SAP MBC cockpit or related configuration nodes, input the bank details, communication protocols, endpoint URLs, and credentials obtained from the banks.
- Define Data Formats and Message Types: Specify the message types to be exchanged (e.g., payment initiation messages like pain.001, payment status reports like pain.002, account statement messages like camt.053). Ensure adherence to agreed-upon standards.
Best Practices for Testing and Validating Bank Connectivity Configurations
Thorough testing and validation are indispensable for ensuring the integrity and reliability of your SAP MBC implementation. Skipping or rushing this phase can lead to erroneous payments, reconciliation issues, and significant financial risks. A comprehensive testing strategy builds confidence in the system’s ability to perform as expected.The validation process should encompass not only the technical connectivity but also the accuracy and completeness of the data being exchanged.
- Unit Testing of Individual Components: Test each configured interface and mapping within SAP CPI and the SAP system independently to ensure they function correctly in isolation.
- End-to-End Connectivity Testing: Simulate real-world scenarios by sending test payment messages from SAP to the bank and receiving test account statements back. Verify that data flows through the entire chain without errors.
- Data Format Validation: Use validation tools or manual checks to ensure that the data exchanged conforms to the specified ISO 20022 standards or other agreed-upon formats. Incorrect formatting is a common cause of rejection.
- Security Protocol Verification: Confirm that all security measures, including encryption and digital certificates, are correctly implemented and functioning. This is critical for protecting sensitive financial data.
- Transaction Volume and Performance Testing: If possible, conduct tests with realistic transaction volumes to assess the system’s performance and identify potential bottlenecks under load.
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Involve business users to perform UAT, simulating their daily tasks. This ensures the solution meets business requirements and is user-friendly.
- Error Handling and Exception Management Testing: Test how the system handles errors, such as invalid data, connectivity issues, or bank rejections. Ensure that appropriate notifications and fallback procedures are in place.
“Effective testing is not about finding bugs; it’s about building confidence in the system’s ability to deliver accurate and timely financial transactions.”
Checklist for Essential Post-Implementation Monitoring and Maintenance
The implementation of SAP MBC is not the end of the journey; it marks the beginning of a continuous cycle of monitoring and maintenance. Proactive oversight ensures the ongoing health and efficiency of your bank connectivity, minimizing disruptions and maximizing the return on your investment. Regular checks and updates are essential to adapt to evolving banking standards and security protocols.This checklist provides a framework for the critical activities required to keep your SAP MBC solution running optimally.
- Regular Monitoring of Communication Channels: Continuously monitor the status of all bank connections for errors, latency, or unexpected downtime. Utilize SAP MBC dashboards and alerts.
- Review of Transaction Logs and Error Reports: Periodically review transaction logs and error reports generated by SAP MBC, SAP CPI, and the SAP system to identify and resolve any recurring issues promptly.
- Periodic Security Audits and Certificate Renewals: Conduct regular security audits to ensure compliance with internal policies and industry best practices. Manage and renew digital certificates before they expire.
- Update and Patch Management: Stay informed about SAP support packages, SAP CPI updates, and any patches released by SAP or your banking partners. Apply them in a timely manner to maintain system security and performance.
- Performance Analysis and Optimization: Analyze system performance metrics to identify areas for optimization. This could involve tuning integration flows or reviewing system resource utilization.
- Regular Reconciliation of Bank Statements: Ensure that automated reconciliation processes are running smoothly and that any discrepancies are investigated and resolved swiftly.
- Documentation Updates: Maintain up-to-date documentation for all configurations, integration flows, and operational procedures. This is vital for knowledge transfer and troubleshooting.
- Change Management Process: Establish a robust change management process for any modifications to bank connections, integration scenarios, or system configurations.
- Regular Communication with Banking Partners: Maintain open lines of communication with your banks to stay informed about any upcoming changes to their systems, protocols, or security requirements.
Key Features and Functionalities of SAP MBC
SAP Multi-Bank Connectivity (MBC) is not merely a conduit for data; it’s a sophisticated platform designed to streamline and secure financial operations. Its core strength lies in its ability to provide a unified, standardized interface for interacting with a multitude of banking partners, thereby abstracting the complexities of diverse bank-specific protocols and formats. This section delves into the critical features that empower organizations to achieve greater efficiency, transparency, and control over their financial workflows.The platform’s architecture is built to handle the end-to-end lifecycle of payment and reconciliation processes, offering granular control and robust automation.
By centralizing these critical functions, SAP MBC minimizes manual intervention, reduces the risk of errors, and significantly accelerates financial closing cycles. Understanding these capabilities is paramount for any organization looking to leverage its full potential.
Outbound Payment Processing and Reconciliation Capabilities
SAP MBC offers a comprehensive suite of functionalities for managing outbound payments, from initiation to final reconciliation. This includes the ability to generate payment instructions in various formats, ensuring compatibility with diverse banking systems. The platform automates the creation and transmission of payment files, significantly reducing the manual effort typically associated with this process. Furthermore, it provides real-time status updates on payment execution, allowing treasury and finance teams to monitor the progress of transactions and proactively address any potential issues.Reconciliation is a cornerstone of financial integrity, and SAP MBC excels in this area by automating the matching of outgoing payments with bank confirmations.
The system facilitates the import of payment confirmations from banks, enabling an automated comparison against outgoing payment proposals. This significantly reduces the time and resources spent on manual reconciliation, minimizing discrepancies and accelerating the financial close. The platform’s intelligent matching algorithms can handle complex scenarios, improving accuracy and providing a clear audit trail for all payment activities.
Inbound Bank Statement Processing and Exception Handling
The processing of inbound bank statements is a critical yet often labor-intensive task. SAP MBC transforms this by enabling the automated import and processing of electronic bank statements from multiple banking partners. The platform supports various bank statement formats, including MT940, CAMT.053, and proprietary formats, ensuring broad compatibility. Upon import, SAP MBC automatically posts the transactions to the relevant general ledger accounts, significantly reducing manual data entry and associated errors.Exception handling is a key differentiator for SAP MBC.
The system is designed to identify and flag transactions that cannot be automatically processed, such as discrepancies in amounts, missing information, or unmatched transactions. These exceptions are presented to users through intuitive dashboards and alerts, allowing for swift investigation and resolution. The platform provides tools for users to analyze the root cause of exceptions and to define rules for future automated handling, thereby continuously improving the straight-through processing rate.
Support for Various Payment Methods and Formats
A significant advantage of SAP MBC is its inherent flexibility in supporting a wide array of payment methods and formats. This adaptability is crucial in today’s globalized business environment where different regions and countries mandate specific payment instruments and data structures. Whether it’s domestic transfers, international wire transfers (SWIFT), direct debits, or other specialized payment types, SAP MBC can be configured to accommodate them.The platform’s ability to support diverse formats is equally important.
It can process and generate payment files in numerous standards, including:
- ISO 20022 (e.g., CAMT and pain messages)
- SWIFT FIN messages (e.g., MT103, MT940)
- Local country-specific formats
This broad support ensures that organizations can seamlessly connect with their banking partners, regardless of the preferred communication protocols and data structures employed by each bank. This standardization simplifies integration and reduces the need for costly custom development for each banking relationship.
Reporting and Monitoring Tools
Visibility and control are paramount in financial management, and SAP MBC provides robust reporting and monitoring tools to achieve this. The platform offers a range of standard reports that provide insights into payment volumes, processing times, exception rates, and bank connectivity status. These reports are crucial for performance analysis, identifying bottlenecks, and ensuring compliance.Key monitoring features include:
- Real-time dashboards displaying the status of payment runs and bank statement processing.
- Alerts for critical events, such as connectivity issues or failed transactions.
- Audit trails for all transactions, providing a comprehensive history for compliance and dispute resolution.
- Performance metrics to track straight-through processing rates and identify areas for optimization.
These tools empower finance teams to proactively manage their banking operations, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions to enhance efficiency and reduce risk.
Integration Points with Other SAP Modules
The true power of SAP MBC is amplified by its seamless integration with other core SAP modules, creating a unified financial ecosystem. This integration ensures data consistency and eliminates redundant data entry, leading to significant operational efficiencies.Key integration points include:
- SAP S/4HANA Finance: Real-time posting of payments and bank statements directly into the General Ledger (FI-GL), Accounts Payable (AP), and Accounts Receivable (AR) modules. This ensures that financial records are always up-to-date and accurate.
- SAP Treasury and Risk Management (TRM): Enables the automated processing of treasury transactions, including money market deals, foreign exchange transactions, and derivatives, directly from bank confirmations. This streamlines cash management and improves liquidity forecasting.
- SAP Cash Management: Provides enhanced visibility into cash positions by consolidating bank account information and transaction flows from multiple banks. This facilitates more effective cash pooling and investment strategies.
- SAP Business Partner: Manages bank master data and relationships, ensuring consistent and accurate information across the system.
This deep integration ensures that financial data flows smoothly across the organization, enabling a holistic view of financial operations and supporting strategic decision-making.
Downloading and Accessing Resources for SAP MBC

Navigating the SAP ecosystem for critical documentation and support can often feel like an expedition. This section demystifies the process of acquiring the essential resources for a successful SAP Multi-Bank Connectivity (MBC) implementation, ensuring you have the authoritative information at your fingertips. We will delve into the primary repositories for official guides, the indispensable role of SAP Notes, and the vibrant learning and community platforms that foster expertise.The digital landscape of SAP resources is vast, but understanding the typical entry points for documentation and guides is paramount.
These official sources are curated to provide the most accurate and up-to-date information, forming the bedrock of any successful technical endeavor.
Official SAP Documentation Sources
The primary repository for official SAP documentation is the SAP Help Portal. This comprehensive online library hosts user guides, administration guides, configuration guides, and technical specifications for virtually all SAP products, including SAP MBC. It is meticulously organized by product and version, allowing users to pinpoint the exact documentation they require. Beyond the Help Portal, SAP’s official product pages often provide links to key documentation and overviews.
For enterprise-level customers, access to the SAP Service Marketplace (now largely integrated into SAP for Me) previously offered a gateway to more detailed technical documents, though the primary access point for general documentation remains the Help Portal.
SAP Notes and Support Resources
SAP Notes are critical bulletins that address specific issues, provide bug fixes, offer performance enhancements, and detail important configuration prerequisites or changes. For SAP MBC, relevant SAP Notes are indispensable for troubleshooting and ensuring optimal system performance. These are exclusively accessible through the SAP Support Portal (also accessible via SAP for Me). Searching for SAP Notes requires a valid SAP Service Marketplace user ID.
It is advisable to regularly check for new or updated Notes related to your specific SAP MBC version and the connected banking services.
Training Materials and Learning Platforms
Acquiring the necessary skills for SAP MBC implementation and management is facilitated through structured learning pathways. SAP offers a range of training materials and dedicated learning platforms designed to equip professionals with the required knowledge.
- SAP Learning Hub: This is SAP’s primary subscription-based platform offering access to a vast library of e-learning courses, hands-on practice systems, and expert-led sessions. Courses specifically covering SAP Cash Management, Treasury, and increasingly, Multi-Bank Connectivity are regularly updated.
- SAP Community: While not a formal training platform, the SAP Community is an invaluable resource for self-directed learning through articles, blogs, and Q&A forums.
- Official SAP Training Courses: SAP also offers instructor-led training courses, both virtual and in-person, which can be booked through the SAP Training website. These often provide a more in-depth and interactive learning experience.
User Communities and Forums
Engaging with a community of peers and experts can significantly accelerate problem-solving and knowledge acquisition. For SAP MBC, several avenues exist for users to connect and share insights.
- SAP Community: This is the most prominent platform where users can ask questions, share experiences, and find solutions posted by other SAP professionals, including SAP employees and experienced consultants. Dedicated groups or tags related to SAP Treasury and Cash Management often host discussions relevant to MBC.
- LinkedIn Groups: Various professional networking groups on LinkedIn are dedicated to SAP topics, including treasury and finance solutions. These can be valuable for informal discussions and networking.
- Partner and Vendor Forums: If you are working with an SAP implementation partner or a specific banking software vendor that integrates with SAP MBC, they may host their own user forums or community spaces.
Technical Guides and Implementation Blueprints
For detailed, step-by-step guidance on implementing and configuring SAP MBC, technical guides and implementation blueprints are essential. These documents often provide configuration steps, data flow diagrams, and best practices.
- SAP Help Portal: As mentioned, this is the primary source for official configuration guides and technical manuals. Look for sections dedicated to SAP S/4HANA Finance, Treasury and Risk Management, and specifically, Cash Management.
- SAP Notes (again): While primarily for issue resolution, some SAP Notes can contain detailed technical instructions or configuration parameters that function as mini-blueprints for specific scenarios.
- SAP Best Practices Explorer: This tool provides access to pre-packaged business process solutions, including implementation content for various SAP modules. While not always directly an MBC implementation guide, it can offer foundational configurations for related treasury processes.
- Partner Documentation: Implementation partners often develop their own proprietary documentation and accelerators based on their experience with SAP MBC. Inquire with your implementation partner for any available resources.
When searching for these resources, employing specific s such as “SAP Multi-Bank Connectivity,” “SAP S/4HANA Cash Management,” “SAP Bank Communication Management,” along with your specific SAP version and the names of the banks or payment formats you intend to use, will yield more precise results.
Advanced Considerations and Future Trends in SAP MBC: A Practical Guide To Sap Multi-bank Connectivity Book Download

As SAP Multi-Bank Connectivity (MBC) matures, its landscape is increasingly shaped by the overarching digital transformation trends. This section delves into the critical advanced considerations and emerging trends that will define the future of bank communication within the SAP ecosystem, moving beyond foundational implementation to strategic integration and forward-looking capabilities.The modern enterprise operates in a dynamic environment where agility and real-time insights are paramount.
SAP MBC, therefore, is not static but evolves to meet these demands, integrating with cutting-edge technologies and adapting to new regulatory and operational paradigms. This proactive evolution ensures that businesses can maintain a competitive edge by optimizing their financial operations and enhancing their resilience.
Cloud-Based Solutions in Modern Bank Connectivity
The migration of business processes to the cloud has fundamentally altered how organizations approach integration, and bank connectivity is no exception. Cloud-based solutions offer a more flexible, scalable, and often cost-effective alternative to traditional on-premise implementations. SAP MBC itself is increasingly leveraging cloud infrastructure, facilitating easier deployment, updates, and management. This shift allows businesses to bypass the complexities of managing on-premise servers and middleware, focusing instead on the strategic benefits of streamlined financial communication.
The agility of cloud solutions also enables faster integration with new banking partners and the adoption of emerging financial technologies.
“Cloud-native integration platforms are becoming the de facto standard for connecting disparate systems, including financial institutions, due to their inherent scalability and reduced operational overhead.”
Integration of Real-Time Payment Capabilities with SAP MBC
The acceleration of financial transactions is a defining characteristic of modern commerce. Real-time payments (RTP) are no longer a niche offering but a critical expectation for businesses aiming for enhanced liquidity management and improved customer experience. SAP MBC is evolving to natively support and facilitate the integration of RTP capabilities. This involves enabling direct connections to payment rails that support instant clearing and settlement, allowing for immediate visibility into cash positions and faster processing of receivables and payables.
The integration goes beyond mere transaction transmission; it encompasses the robust handling of confirmations, status updates, and reconciliation data in near real-time.Consider a scenario where a company can initiate a payment to a supplier and receive immediate confirmation of funds transfer and debits, all managed through SAP MBC. This dramatically reduces processing times, minimizes the need for manual reconciliation, and frees up working capital by enabling more precise cash flow forecasting.
Evolving Security Standards and Their Impact on Bank Communication
Security remains a non-negotiable aspect of financial data exchange. As communication channels become more digitized and interconnected, the sophistication of security threats also increases. SAP MBC is designed to adhere to stringent, evolving security standards to protect sensitive financial information. This includes leveraging modern encryption protocols, robust authentication mechanisms, and compliance with international regulations such as PSD2 (Payment Services Directive 2) and other data privacy mandates.
The impact of these evolving standards is a continuous requirement for updating security configurations, implementing multi-factor authentication, and ensuring end-to-end data integrity throughout the communication lifecycle.Key security considerations include:
- Data Encryption: Implementing strong encryption algorithms for data in transit and at rest.
- Authentication and Authorization: Utilizing secure methods for verifying the identity of both the SAP system and the banking institution, along with granular access controls.
- Compliance with Regulations: Adhering to global and regional financial regulations that govern data privacy, security, and transaction reporting.
- Fraud Detection and Prevention: Integrating with or enabling capabilities for detecting anomalous transaction patterns.
Potential Enhancements and Future Roadmap Items for SAP MBC
The roadmap for SAP MBC is driven by the need to anticipate and address future business requirements. Potential enhancements focus on expanding its capabilities to support a broader range of financial instruments, streamlining reconciliation processes further, and incorporating advanced analytics. Future developments are likely to include deeper integration with open banking APIs, enhanced support for cryptocurrencies and blockchain-based financial instruments, and more sophisticated fraud detection and prevention tools embedded within the connectivity layer.
Furthermore, advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning could be leveraged to provide predictive insights into cash flows, optimize payment routing, and automate exception handling.
Comparison of Different Connectivity Strategies and Their Suitability for Various Business Sizes
Choosing the right connectivity strategy is crucial and depends heavily on a company’s size, complexity, and specific banking relationships.
| Connectivity Strategy | Description | Suitability | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct SWIFT/EDI Connections | Establishing direct connections with banks using established protocols like SWIFT or EDI standards. | Large enterprises with high transaction volumes and established banking relationships. | High level of control, robust security, standardized communication. | Complex setup and maintenance, high initial investment, can be rigid. |
| SAP Multi-Bank Connectivity (MBC) Platform | A centralized platform provided by SAP that acts as an intermediary, connecting to multiple banks through standardized interfaces. | Medium to large enterprises seeking to simplify and centralize bank communication across various financial institutions. | Simplified management, reduced complexity, faster onboarding of new banks, standardized reporting. | Reliance on SAP’s platform and its supported banks, potential subscription costs. |
| Third-Party Connectivity Solutions | Leveraging specialized vendors that offer connectivity services to a wide range of banks, often integrating with SAP via APIs. | Businesses of all sizes looking for flexibility, broad bank coverage, and specialized features, especially those with complex or international banking needs. | Extensive bank network, rapid deployment, specialized expertise, often more agile than direct connections. | Additional vendor costs, integration layer complexity, dependency on the third-party provider. |
| API-Based Connectivity | Direct integration with banks via their Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), often facilitated by open banking initiatives. | Forward-thinking businesses of all sizes, particularly those embracing digital transformation and open banking. | Real-time data exchange, flexibility, innovation potential, reduced reliance on traditional intermediaries. | Requires robust API management, bank API availability and standardization can vary, ongoing development needs. |
For small businesses, a simpler approach like direct integration with a primary bank via file upload or a basic API might suffice. Medium-sized businesses often benefit from the consolidation and efficiency offered by SAP MBC or a tailored third-party solution. Large enterprises with diverse and high-volume banking needs may opt for a combination of strategies, potentially using SAP MBC as a central hub while retaining direct or API-based connections for specific critical relationships or emerging technologies.
The trend is undeniably towards more integrated, real-time, and API-driven solutions, regardless of business size, as the benefits of agility and efficiency become increasingly apparent.
End of Discussion

So, whether you’re just dipping your toes into SAP Multi-Bank Connectivity or looking to level up your game, this guide is your ultimate companion. It’s all about making complex financial tasks feel as easy as catching a wave, ensuring your business runs smoothly and securely, leaving you more time to soak up that island life.
Clarifying Questions
Where can I actually download the book?
You’ll typically find links to download resources or purchase the book on official SAP Press websites, authorized online bookstores, or through SAP’s partner channels. Keep an eye out for specific download sections or product pages.
Is this book suitable for beginners with no SAP experience?
While the book aims to be practical, a basic understanding of SAP financial modules would be beneficial. However, it does cover foundational concepts to help those new to MBC get up to speed.
What are the system prerequisites for implementing SAP MBC as described in the book?
The book details necessary SAP system requirements, authorizations, and potentially specific modules like SAP S/4HANA or SAP ECC. Always check the latest SAP documentation for the most current prerequisites.
Does the book cover real-time connectivity options?
Yes, advanced sections likely touch upon modern connectivity methods, including real-time capabilities, and discuss their integration with SAP MBC.
Are there any free resources mentioned for learning SAP MBC besides the book download?
The book will likely point you towards SAP Notes, official SAP documentation, training platforms, and user communities where additional free resources and discussions can be found.




