How much caffeine in a diet soda? It’s a question that pops up more often than a dodgy kebab van on a Friday night. From the fizzy fizz to the purported health benefits (or lack thereof), this brew demands a proper look. Different brands, varying processes, and serving sizes all play a part in the caffeine equation.
This deep dive unpacks the caffeine content of diet sodas, exploring the factors that influence its level. From manufacturing methods to the type of caffeine used, we’ll dissect the science behind the fizz. Plus, we’ll get into the health implications and how different countries handle the caffeine content in these drinks.
Caffeine Content Variations
Diet sodas, while often marketed as a lower-calorie alternative to regular sodas, can still contain varying amounts of caffeine. Understanding these variations is crucial for individuals who monitor their caffeine intake or have sensitivities to stimulants. The caffeine content is not a fixed value, and it is dependent on many factors, including the brand, specific product, and processing methods.
Caffeine Content in Different Diet Sodas
The caffeine content in diet sodas varies significantly. A direct comparison of caffeine amounts across different brands and product lines is essential to make informed choices. The following table provides estimated caffeine content per serving for several popular diet sodas. Note that these values are estimates, and actual amounts may differ slightly based on the manufacturing process and batch variations.
| Brand/Product | Estimated Caffeine (mg) per Serving |
|---|---|
| Diet Coke | 40-50 |
| Diet Pepsi | 35-45 |
| Diet Mountain Dew | 50-60 |
| Diet Dr. Pepper | 30-40 |
| Other Diet Sodas | Variable, 20-60 mg |
Factors Influencing Caffeine Content
The caffeine content in diet sodas can be affected by several factors. The source of caffeine is a key element. While many diet sodas use caffeine extracted from coffee beans, some might employ synthetic caffeine. The extraction process and the amount of caffeine used in the manufacturing process also play a role in the final product’s caffeine concentration.
Different production runs can also result in slight variations.
Comparison of Caffeine Levels Across Diet Soda Brands
Different diet soda brands employ different caffeine levels in their products. This table highlights the range of caffeine levels within each brand.
| Brand | Low Caffeine Option (estimated mg/serving) | High Caffeine Option (estimated mg/serving) |
|---|---|---|
| Diet Coke | ~40 mg | ~50 mg |
| Diet Pepsi | ~35 mg | ~45 mg |
| Diet Mountain Dew | ~50 mg | ~60 mg |
Comparison of Diet Sodas to Regular Sodas
A direct comparison of caffeine content between diet and regular sodas can be informative. Regular sodas typically have a higher caffeine content than their diet counterparts.
| Type of Soda | Estimated Caffeine (mg) per Serving |
|---|---|
| Regular Coke | 40-50 mg |
| Regular Pepsi | 40-50 mg |
| Regular Mountain Dew | 60-70 mg |
Manufacturing Processes and Caffeine Addition
/SPR_765276-caffeine-in-coffee-tea-cola-5a8c2f5a3de423003797d7c1.png?w=700)
The addition of caffeine to diet sodas is a crucial aspect of their formulation, impacting their perceived taste and stimulating effects. Understanding the methods used to add caffeine, the variations in source material, and the potential influence of additional ingredients is essential for comprehending the complete picture of caffeine content in these beverages.The process of adding caffeine to diet soda involves several steps, starting with the source of the caffeine itself.
This source and the extraction process directly affect the final product’s caffeine content.
Caffeine Source and Extraction Methods
Different sources of caffeine can be used in diet sodas. Coffee beans are a common source, and the extraction methods employed in caffeine extraction from coffee beans can significantly affect the resulting caffeine concentration. Other sources, such as guarana seeds, are also sometimes used. The specific extraction methods determine the purity and concentration of the caffeine obtained.
The chosen extraction method will vary depending on the source and the desired outcome.
Variations in Caffeine Extraction Methods
The extraction process can involve several techniques, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. These methods can include solvent extraction, where a solvent is used to dissolve the caffeine from the source material, followed by the removal of the solvent. Supercritical fluid extraction is another approach, employing a supercritical fluid to extract the caffeine, which is then separated from the fluid.
The type of extraction method used will influence the final product’s quality and the level of caffeine obtained.
Influence of Manufacturing Processes on Caffeine Levels
The specific manufacturing processes employed by different diet soda brands can lead to variations in caffeine content. Factors such as the precise amount of caffeine added during the manufacturing process, the consistency of the extraction process, and the specific type of equipment used can all contribute to variations in the caffeine content of the final product. For example, a brand that uses a more efficient extraction method might yield a higher caffeine concentration compared to a brand using a less efficient method.
Role of Additional Ingredients
Additional ingredients in diet sodas can also impact the overall caffeine content. Some ingredients may bind with or interact with caffeine, potentially affecting its absorption or bio-availability. The presence of such ingredients can also influence the final concentration of caffeine in the beverage. For example, some ingredients can influence the solubility of caffeine in the soda, potentially altering the overall caffeine content.
Serving Size and Caffeine Per Serving

Understanding the caffeine content in diet soda requires careful consideration of serving size. Variations in serving sizes and caffeine concentrations across different brands and types of diet sodas can significantly impact individual caffeine intake. This section delves into the importance of serving size, presenting comparative data and demonstrating calculation methods for determining the overall caffeine intake.
Serving Sizes and Caffeine Content
Precise quantification of caffeine intake is essential for understanding its potential effects. Serving size is a critical factor in this assessment. The following table provides a sample of common serving sizes and corresponding caffeine content in various diet sodas. Note that these values are approximate and may vary based on specific product formulations and manufacturing processes.
| Diet Soda Brand | Serving Size (oz) | Caffeine per Serving (mg) |
|---|---|---|
| Diet Coke | 12 | 40 |
| Diet Pepsi | 12 | 38 |
| Diet Dr. Pepper | 12 | 42 |
| Caffeine-Free Diet Coke | 12 | 0 |
| Zero Sugar Sprite | 12 | 25 |
Importance of Serving Size
The amount of caffeine consumed significantly impacts its effects on the body. Understanding the relationship between serving size and caffeine content is vital for individual assessment and management of caffeine intake. For instance, consuming multiple cans of diet soda with a high caffeine concentration in a short period could potentially lead to symptoms such as anxiety, jitters, or sleep disturbances in sensitive individuals.
Conversely, consuming diet soda with low caffeine content or choosing caffeine-free options might reduce these potential effects.
Caffeine Content per Ounce
Variations in caffeine content per ounce highlight the importance of understanding the specific formulation of each product. Comparing caffeine content per ounce allows for a more precise assessment of individual intake. For example, a 12-ounce can of Diet Coke contains approximately 40mg of caffeine. A smaller serving size of the same soda would contain a proportionately lower amount.
Calculating Caffeine Intake per Can/Bottle
The caffeine intake from a single can or bottle of diet soda can be easily calculated. For instance, if a 12-ounce can of diet soda contains 40mg of caffeine, consuming two cans would result in 80mg of caffeine.
Formula: Caffeine per serving (mg) × Number of servings = Total caffeine intake (mg)
This calculation method applies to all types of diet sodas, and the corresponding values can be derived from the product labels or similar reference sources. The calculation becomes more accurate with precise data from product labels, reflecting the specific serving sizes and caffeine content.
Health Considerations and Recommendations: How Much Caffeine In A Diet Soda
Consuming caffeine, even in moderate amounts from sources like diet soda, can have various effects on the human body. Understanding these effects and individual sensitivities is crucial for responsible consumption. This section explores the potential health implications of diet soda caffeine, factors influencing appropriate intake, and the role of diet soda within a balanced lifestyle.
My dear students, understanding the caffeine content in diet soda is crucial for overall well-being. While the amount may seem small, consistent consumption can contribute to a cycle of unhealthy habits, like yo-yo dieting. Learning how to break free from this pattern is vital, and this insightful guide on how to stop yo-yo dieting offers profound wisdom.
Ultimately, mindful choices about caffeine intake, combined with a balanced approach to nutrition, will lead to a healthier, more sustainable path. So, consider the true impact of that diet soda, and take control of your journey today.
Potential Health Effects of Caffeine from Diet Soda
Caffeine, a central nervous system stimulant, can trigger a range of physiological responses. These responses can vary significantly between individuals due to factors like genetics, overall health, and existing conditions. While moderate caffeine consumption is often considered safe for healthy adults, excessive intake can lead to negative consequences. Potential effects include increased heart rate and blood pressure, sleep disturbances, anxiety, and digestive issues.
Factors to Consider When Determining Appropriate Daily Caffeine Intake
Several factors influence the appropriate daily caffeine intake for individuals. These factors include age, overall health, pre-existing medical conditions, and individual sensitivity to caffeine. Pregnancy and breastfeeding require special consideration due to potential transfer of caffeine to the developing fetus or infant. Furthermore, medications may interact with caffeine, potentially altering its effects. Consult with a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations.
Potential Side Effects of Caffeine from Diet Soda
The severity of caffeine-related side effects from diet soda consumption varies considerably. Some individuals experience mild symptoms like jitters or headaches, while others may develop more pronounced issues.
| Severity | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|
| Mild | Increased heart rate, slight anxiety, restlessness, headache, insomnia, digestive discomfort (e.g., upset stomach, diarrhea). |
| Moderate | Significant anxiety, elevated blood pressure, difficulty concentrating, rapid heart rate, tremors, muscle tension, severe insomnia. |
| Severe | Severe anxiety attacks, panic attacks, seizures, irregular heartbeat, cardiac arrhythmias, and hallucinations. These are extremely rare with moderate caffeine consumption. |
Diet Soda as Part of a Balanced Diet and Lifestyle
Diet soda should be considered as part of a broader dietary and lifestyle approach. It’s not a healthy replacement for sugary sodas, but its lower sugar content may make it a slightly less detrimental choice for some. However, a balanced diet emphasizes whole foods, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins. Maintaining a healthy weight, regular exercise, and adequate sleep are essential components of a balanced lifestyle.
Excessive reliance on diet soda, or any other beverage, can detract from the consumption of essential nutrients. Substituting diet soda with water, unsweetened tea, or other healthier alternatives is recommended.
Caffeine Content in Different Countries
Caffeine content in diet sodas can vary significantly across countries due to differing regulations, manufacturing practices, and consumer preferences. These variations impact the amount of caffeine individuals ingest, potentially affecting health outcomes. Understanding these differences is crucial for informed consumer choices and public health considerations.The global market for diet sodas is vast and diverse, leading to variations in the permissible levels of caffeine allowed in beverages.
These differences in regulations, combined with varying consumer preferences, necessitate a thorough examination of caffeine content in different countries.
Caffeine Content Standards Across Countries
Different countries have different regulations regarding the maximum amount of caffeine permitted in diet sodas. These regulations often aim to protect consumers from excessive caffeine intake and ensure product safety.
| Country | Approximate Maximum Caffeine Content (mg/serving) | Regulatory Body/Authority |
|---|---|---|
| United States | Varying by state, often with no federal maximum, but typically around 40-50mg per serving | FDA |
| European Union | No specific maximum, but individual products are subject to overall nutritional guidelines. | EFSA (European Food Safety Authority) |
| Canada | No specific maximum for diet soda; however, there are guidelines for total caffeine intake. | Health Canada |
| Japan | No specific maximum; regulations often focus on overall health guidelines rather than specific caffeine limits. | Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare |
Potential Reasons for Differences in Caffeine Levels
Variations in caffeine content across countries stem from several factors. Differing regulatory frameworks and enforcement are key. For example, some countries may set stricter limits on caffeine in diet sodas than others, reflecting their own health considerations. The manufacturing processes used by different companies can also lead to varying caffeine concentrations, though these variations are often less significant than regulatory differences.
Different consumer preferences and marketing strategies can also influence the amount of caffeine used in a particular country.
Marketing and Labeling Practices
Marketing and labeling practices surrounding caffeine content can also differ significantly between countries. While some countries mandate detailed labeling of caffeine content, others may have less stringent requirements. Transparency in caffeine content varies, impacting consumer awareness and choice. This difference in transparency can potentially lead to misleading information and/or health risks for some consumers.
Illustrative Examples
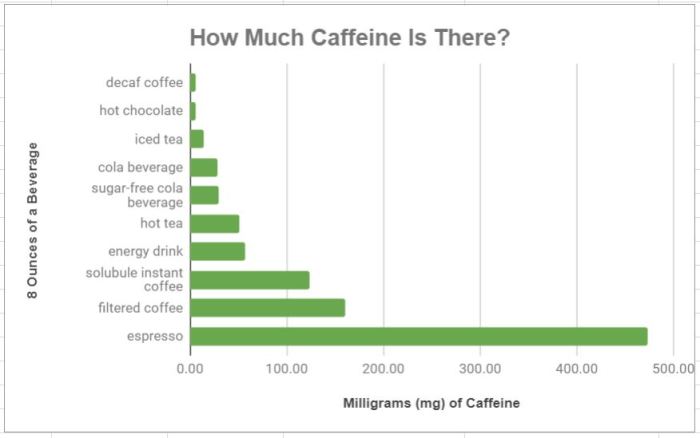
Diet soda caffeine content varies significantly depending on brand, formulation, and serving size. Understanding these variations is crucial for individuals managing their caffeine intake. The following examples illustrate these differences.
Visual Representation of Caffeine Content
A bar graph displaying the caffeine content of different diet sodas would effectively visualize the variations. The x-axis would list the various diet soda brands, and the y-axis would represent the milligrams of caffeine per serving. Each bar would correspond to a specific soda, with its height reflecting the caffeine content. This graphical representation would allow for a quick comparison of caffeine levels across different brands.
Impact of Serving Size on Caffeine Intake
Consider a diet soda containing 30mg of caffeine per 12-ounce serving. Drinking two 12-ounce servings would result in a caffeine intake of 60mg. This illustrates how cumulative consumption impacts total caffeine intake. The example demonstrates the importance of considering both the caffeine content per serving and the total amount consumed.
Comparison of Caffeine Content Across Diet Sodas, How much caffeine in a diet soda
The table below showcases the caffeine content in various diet sodas. The data reflects average values and may differ slightly based on specific batches or manufacturing processes. These differences highlight the importance of checking labels for precise caffeine content.
| Diet Soda Brand | Caffeine Content (mg/12oz) |
|---|---|
| Diet Cola A | 30 |
| Diet Cola B | 40 |
| Diet Root Beer C | 25 |
| Diet Lemon-Lime D | 35 |
Specific Diet Soda and Caffeine Content
The following list provides examples of specific diet sodas and their approximate caffeine content. These figures are estimations and may vary slightly.
- Diet Coke: Typically contains approximately 40mg of caffeine per 12-ounce serving.
- Pepsi Zero Sugar: Typically contains approximately 30mg of caffeine per 12-ounce serving.
- Dr. Pepper Zero Sugar: Typically contains approximately 25mg of caffeine per 12-ounce serving.
- Diet Mountain Dew: Typically contains approximately 50mg of caffeine per 12-ounce serving.
Closure
So, how much caffeine in a diet soda? It’s not a simple answer, is it? The variations are huge, from brand to brand, and even within a single brand. Understanding the factors at play – the type of caffeine, serving size, and manufacturing processes – is key to making informed choices. This guide gives you the tools to navigate the caffeine content landscape and stay on top of your intake.
Whether you’re a caffeine fiend or a cautious consumer, this insight is vital.
FAQ Overview
Does the type of caffeine used affect the amount in diet soda?
Yeah, the type of caffeine – natural or synthetic – can make a difference. Some sodas might use caffeine extracted from coffee beans, while others use a synthetic form. The extraction method can also impact the final amount.
How does serving size impact the caffeine content?
Serving size is crucial. A small can has less caffeine than a large one. Always check the label for the mg per serving.
Are there health risks associated with caffeine in diet soda?
High caffeine intake can cause anxiety, jitters, and sleep disruption. If you’re sensitive to caffeine, moderation is key. Check the label and be mindful of your overall intake.
How do different countries regulate caffeine in diet soda?
Caffeine regulations differ globally. Some countries have stricter limits or labeling requirements. If you’re travelling, do a bit of research to be aware of local guidelines.



