What muscles does benching workout? This question is at the heart of many fitness enthusiasts’ journeys as they seek to build strength and sculpt their upper bodies. The bench press is not just a test of brute force; it’s an intricate dance of muscle engagement that, when performed correctly, can transform not only your physique but also your overall athletic performance.
Whether you’re a seasoned lifter or a beginner, understanding the mechanics of this powerful exercise can enhance your training regimen and help you achieve your fitness goals.
As we dive deeper into the world of the bench press, we’ll explore the primary and secondary muscles activated during this classic lift, the benefits of strengthening these muscles, and how variations of the bench can target different areas for growth. We’ll also discuss common mistakes to avoid and the role of nutrition in muscle development, ensuring that you have a comprehensive understanding of this essential exercise.
Overview of Bench Press

The bench press is a fundamental exercise in strength training, renowned for its ability to develop upper body strength. It primarily targets the pectoral muscles, triceps, and shoulders, making it a staple in many workout regimens. This exercise not only builds muscle mass but also enhances overall functional strength, making it popular among athletes and fitness enthusiasts alike.The mechanics of the bench press involve lying on a bench while lifting a weighted barbell or dumbbells.
The movement consists of lowering the weight to the chest and then pressing it back to the starting position. Proper form and technique are crucial to maximize effectiveness and minimize the risk of injury. Incorrect posture or improper weight selection can lead to muscular imbalances and strains, underscoring the need for education in executing the exercise correctly.
Importance of Proper Form and Technique
Understanding the significance of proper form in bench pressing is vital for both safety and performance. Key elements of proper technique include:
- Feet Placement: Keeping the feet flat on the ground helps to stabilize the body and maintain balance during the lift.
- Grip Width: A grip that is too wide or too narrow can lead to unnecessary strain on the shoulders. A shoulder-width grip is generally recommended for optimal engagement of the chest muscles.
- Back Position: Maintaining a natural arch in the back while keeping the shoulder blades retracted can help support the spine and improve power output.
- Bar Path: The bar should travel in a straight line, coming down to the mid-chest and pressing back up over the shoulders to ensure efficient force generation.
According to data from the International Sports Sciences Association (ISSA), the bench press ranks as one of the top three most performed exercises in strength training programs. Approximately 60% of gym-goers incorporate bench pressing into their routines, emphasizing its widespread acceptance and importance in physical fitness. This popularity can be attributed to its effectiveness in building muscle and strength, as well as its functionality in various sports and daily activities.
When considering your evening routine, you might wonder if it’s okay to workout before bed. Engaging in exercise can actually help release some tension, but check out this article on is it okay to workout before bed for more insights. It’s important to balance relaxation and physical activity to ensure a restful night.
“Proper technique in bench pressing not only maximizes gains in strength but also significantly reduces the risk of injury.”
Primary Muscles Engaged
The bench press is a foundational exercise known for its effectiveness in developing upper body strength. This compound movement primarily targets several key muscle groups, each playing a critical role in executing the lift. Understanding these muscles not only enhances performance but also informs better training practices and injury prevention strategies.The primary muscles worked during the bench press include the pectoralis major and minor, as well as the deltoids.
The pectoralis major, the larger of the two pectoral muscles, is primarily responsible for the pushing motion involved in the bench press. It plays a significant role in shoulder flexion, adduction, and internal rotation. The pectoralis minor, positioned beneath the major, assists in stabilizing the shoulder and contributes to the overall function of the upper body during the lift.
Pectoralis Major and Minor Engagement
The pectoralis major and minor are crucial for effective bench pressing.
- Pectoralis Major: As the primary muscle engaged during the lift, the pectoralis major’s size and strength significantly influence the amount of weight one can press. Its fibers run from the sternum and clavicle to the upper arm, allowing for powerful movements as the arms push the barbell upward.
- Pectoralis Minor: This smaller muscle supports the pectoralis major and aids in the stabilization of the scapulae. Though not the primary mover, its contribution is vital for maintaining proper form and shoulder health during the press.
Deltoid Involvement in the Bench Press
The deltoids, comprising the anterior, lateral, and posterior portions, are significantly involved in the bench press movement.
- Anatomy of the Deltoids: The anterior deltoid is particularly active during the bench press as it assists in shoulder flexion and stabilizes the shoulder joint. The lateral deltoid also contributes, primarily during the initial phase of the lift.
- Role in Stability: The deltoids provide essential stability to the shoulder joint, allowing for a safer and more effective pressing motion. Strengthening these muscles can enhance overall performance and reduce the risk of shoulder injuries during heavy lifts.
“Developing strong pectoral and deltoid muscles is essential for maximizing one’s performance in the bench press.”
Through an understanding of these primary muscle groups, individuals can better tailor their training routines to enhance strength effectively while minimizing injury risk.
Secondary Muscles Involved
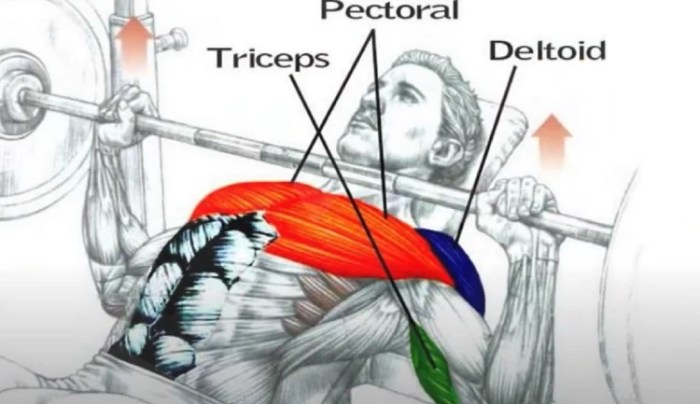
The bench press is not only a primary exercise for building chest strength but also engages several secondary muscles that contribute significantly to the overall lift. Understanding these muscles can provide insights into how to optimize performance and prevent injuries during training. The bench press primarily targets the pectoral muscles; however, several secondary muscles play crucial roles in stabilizing the body and assisting in the lift.
These muscles include the triceps brachii, deltoids, and various stabilizers, including the rotator cuff. Their engagement is vital for both performance and safety during the exercise.
Triceps Engagement
The triceps brachii, located at the back of the upper arm, are heavily involved in the bench press. Their primary function is to extend the elbow joint, allowing for the pressing motion. During the lift, the triceps work synergistically with the pectorals to provide the necessary force to push the barbell away from the chest.
- The triceps are essential for completing the lift, especially during the lockout phase at the top of the movement.
- A well-developed triceps can significantly enhance overall bench press strength, as they contribute to the final push required to finish the lift.
- Strengthening the triceps through accessory exercises, such as tricep dips and skull crushers, can lead to improved performance and heavier lifts in the bench press.
Role of Stabilizers like the Rotator Cuff
Stabilizing muscles play a critical role in maintaining form and joint integrity during the bench press. The rotator cuff, a group of four muscles and their associated tendons, is particularly important for shoulder stability during the movement.
- The rotator cuff helps to keep the shoulder joint stable, reducing the risk of injuries that can occur from heavy lifting.
- Proper engagement of the rotator cuff muscles allows for a safer range of motion, thereby improving lifting mechanics and performance.
- Incorporating exercises that target the rotator cuff, such as external rotations with bands or light weights, can enhance shoulder stability during the bench press.
The combined effort of these secondary muscles ensures not only the effectiveness of the bench press but also the safety and longevity of an athlete’s training regimen.
Benefits of Strengthening These Muscles

Engaging in bench pressing significantly enhances upper body strength by targeting various key muscle groups, which can transform both athletic performance and daily activities. The bench press primarily focuses on the pectoral muscles, deltoids, and triceps, providing a comprehensive workout that fosters muscle growth and functional strength. As a compound exercise, it not only builds mass but also improves overall upper body stability and coordination.
Impact on Athletic Performance
Strengthening the muscles involved in benching can lead to substantial developments in athletic performance. Improved muscle strength translates to enhanced power, speed, and endurance, essential elements in various sports. For athletes, the bench press contributes to better overall performance through:
- Explosive Power: Increased muscle strength facilitates greater force production during explosive movements, such as sprinting or jumping.
- Enhanced Stability: A stronger upper body aids in maintaining balance and control, which is crucial for sports requiring complex movements.
- Injury Prevention: Strengthening muscles reduces the risk of injuries by fortifying joints and improving overall body mechanics.
- Improved Recovery: Enhanced muscle strength can lead to faster recovery times following physical exertion, allowing athletes to train more effectively.
Impact on Daily Activities
Beyond the realm of sports, the benefits of bench pressing extend to everyday life, enhancing overall functional strength. Improved muscle tone from benching can make daily tasks easier and more manageable by:
- Ease of Lifting: Increased strength helps in lifting heavy objects, such as groceries or furniture, with greater ease.
- Posture Support: A stronger upper body contributes to better posture, reducing the likelihood of back pain and improving overall comfort.
- Increased Functional Capacity: Everyday activities that involve pushing or lifting become less strenuous, enhancing quality of life.
- Enhanced Confidence: Improved muscle tone can lead to a more positive self-image, boosting confidence in physical appearances and capabilities.
“Strengthening the muscles used in benching not only enhances athletic performance but also significantly improves the quality of everyday life.”
If you’ve just had laser hair removal, you might be curious about your workout routine. It’s generally advisable to wait a bit to ensure your skin heals properly. For detailed advice, check out this article on can i workout after laser hair removal. Taking care of your skin while staying active is essential for a balanced lifestyle!
Variations of the Bench Press
The bench press is a versatile exercise that can be adapted in various ways to target specific muscle groups. Each variation serves as a tool for strength development, and understanding these can optimize workout routines. By adjusting the angle of the bench or the equipment used, lifters can emphasize different areas of the chest, shoulders, and triceps.The three prominent variations of the bench press include the flat bench press, incline bench press, and decline bench press.
Each variation alters the movement mechanics and consequently shifts the focus onto different muscle groups. The following table summarizes the muscle focus for each variation, providing a clear comparison.
| Bench Press Variation | Primary Muscle Focus | Secondary Muscle Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Flat Bench Press | Pectoralis Major | Triceps, Anterior Deltoids |
| Incline Bench Press | Upper Pectoralis Major | Triceps, Anterior Deltoids |
| Decline Bench Press | Lower Pectoralis Major | Triceps, Anterior Deltoids |
Each variation brings its own unique benefits, allowing athletes to tailor their training programs. The flat bench press is commonly seen as the standard, effectively building overall chest mass. The incline bench press targets the upper chest, which is crucial for a balanced physique, while the decline bench press emphasizes the lower chest, often neglected in traditional routines.The choice between using dumbbells or a barbell in bench pressing can significantly influence muscle development.
Dumbbells allow for a greater range of motion and can help in correcting muscle imbalances due to the independent movement of each arm. This can lead to enhanced stabilization and recruitment of the pectoral and shoulder muscles. In contrast, barbells enable the lifter to typically lift heavier weights, promoting overall strength gains and muscle hypertrophy.
“Utilizing both dumbbells and barbells in a bench press regimen can optimize muscle development and prevent plateaus.”
Incorporating variations and alternating between equipment can lead to comprehensive muscle development, ensuring that lifters achieve balanced growth and strength in their upper body workouts.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
The bench press is a fundamental exercise in strength training, yet many lifters make mistakes that can hinder performance and lead to injury. Understanding these common errors and implementing corrective measures is essential for maximizing the benefits of bench pressing while ensuring safety.One of the most frequent errors during bench pressing is improper grip width. A grip that is too wide or too narrow can affect the engagement of the target muscles and increase the risk of shoulder injuries.
Additionally, poor foot placement can lead to instability, preventing the lifter from generating optimal force.
Frequent Errors and Their Consequences
Recognizing and addressing specific mistakes can significantly enhance your bench press performance and reduce injury risk. The following list Artikels common mistakes made during the bench press along with their potential consequences:
- Incorrect Elbow Position: Allowing elbows to flare out too much can lead to shoulder strain and reduced power transfer during the lift.
- Lifting Feet Off the Ground: This disrupts stability, increasing the chance of injury and reducing overall lifting efficiency.
- Not Maintaining a Neutral Spine: An arched or rounded back can strain the lower back and negatively affect lifting form.
- Insufficient Range of Motion: Not lowering the bar to the chest limits muscle engagement and diminishes the efficacy of the exercise.
- Using Excessive Weight: Lifting more than you can handle encourages poor form and heightens the risk of injury.
Corrective Measures for Proper Form
To avoid the common mistakes listed above, it is crucial to adopt corrective measures that ensure proper bench press technique. The following strategies can help maintain form and prevent injuries:
- Practice Grip Width: Experiment with different grip widths to find the optimal position that feels comfortable and effective.
- Engage the Core: Keep your core tight and maintain a neutral spine throughout the lift to enhance stability.
- Keep Feet Flat: Ensure your feet are planted firmly on the ground to maintain a solid base and improve power transfer.
- Monitor Elbow Position: Keep your elbows at a 45-degree angle relative to your body to protect shoulder joints.
- Progress Gradually: Start with lighter weights and focus on form before gradually increasing the load.
Importance of Warm-Up and Mobility Exercises
Incorporating warm-up and mobility exercises into your routine is vital for preventing injuries related to bench pressing. A proper warm-up increases blood flow to the muscles, enhances flexibility, and prepares the body for strenuous activity. Before attempting heavy lifts, consider engaging in dynamic stretches that target the shoulders, chest, and triceps. Additionally, perform specific mobility exercises such as arm circles, shoulder dislocates with a resistance band, or push-ups to activate the muscles involved in the bench press.
“Proper warm-up and mobility work are crucial for maintaining a healthy range of motion and preventing injuries in the long run.”
Including these practices in your regimen will not only enhance performance but also contribute to longevity in your weightlifting journey. Emphasizing the importance of correct form, addressing common mistakes, and prioritizing warm-up activities will ensure a safer and more effective bench press experience.
Incorporating Bench Press into Workout Regimens
Incorporating the bench press into your workout regimen can significantly enhance your upper body strength and muscle mass. However, it’s essential to structure your training effectively to maximize gains and ensure safety. Below, we Artikel a sample workout plan that includes the bench press and accessory exercises, along with tips for progressive overload and the importance of recovery.
Sample Workout Plan with Bench Press
A well-rounded workout plan should include various exercises that target multiple muscle groups. Here’s a sample weekly routine that integrates the bench press:
- Day 1: Upper Body Strength
- Flat Bench Press: 4 sets of 8 reps
- Incline Dumbbell Press: 3 sets of 10 reps
- Bent-over Barbell Row: 3 sets of 8 reps
- Shoulder Press: 3 sets of 10 reps
- Tricep Dips: 3 sets of 12 reps
- Day 2: Lower Body Strength
- Squats: 4 sets of 8 reps
- Deadlifts: 3 sets of 8 reps
- Lunges: 3 sets of 10 reps per leg
- Calf Raises: 3 sets of 15 reps
- Day 3: Active Recovery
- Light Cardio (walking, cycling): 30 minutes
- Stretching/Yoga: 20 minutes
- Day 4: Upper Body Hypertrophy
- Close Grip Bench Press: 3 sets of 10 reps
- Chest Fly: 3 sets of 12 reps
- Pull-ups: 3 sets to failure
- Lateral Raises: 3 sets of 12 reps
- Day 5: Lower Body Hypertrophy
- Leg Press: 4 sets of 10 reps
- Leg Curls: 3 sets of 12 reps
- Step-ups: 3 sets of 10 reps per leg
- Plank: 3 sets of 30 seconds
- Day 6: Full Body Circuit
- Bench Press: 3 sets of 8 reps
- Burpees: 3 sets of 10 reps
- Mountain Climbers: 3 sets of 30 seconds
- Plank Rows: 3 sets of 10 reps
- Day 7: Rest Day
Progressive Overload Techniques
To enhance muscle gains from the bench press, implementing progressive overload is crucial. This concept involves gradually increasing the weight, frequency, or intensity of your workouts. Here are some effective methods to achieve this:
- Increase Weight: Add small increments of weight to your bench press each week. For example, adding 2.5 to 5 pounds can stimulate further muscle growth.
- Increase Reps: Aim to increase the number of repetitions at your current weight. If you can bench press 200 pounds for 8 reps, strive for 9 or 10 reps in subsequent workouts.
- Reduce Rest Time: Decrease the rest periods between sets to increase intensity, which can lead to muscle hypertrophy.
- Vary the Tempo: Experiment with different lifting tempos (e.g., slower eccentric phases) to challenge your muscles in new ways.
- Incorporate Different Variations: Include variations of the bench press, such as incline or decline bench press, to target muscles differently.
The Importance of Recovery and Rest Days
Recovery is a vital aspect of any workout regimen, especially when focusing on heavy lifts like the bench press. Muscles require time to repair and grow stronger after intense training.
Many folks often ask if sweating during a workout is good. It’s a sign that your body is working hard, helping with detoxification. Want to learn more about its benefits? Take a look at this guide on is sweating during workout good. Embracing that sweat can enhance your fitness journey!
- Muscle Repair: After workouts, muscles undergo microscopic tears which need time to heal. Adequate rest helps facilitate this process.
- Preventing Overtraining: Overtraining can lead to fatigue, reduced performance, and injury. Incorporating rest days mitigates this risk.
- Hormonal Balance: Rest allows for hormonal balance, including testosterone and growth hormone, which are essential for muscle growth.
- Performance Improvement: Adequate recovery has been shown to improve subsequent performance. This can lead to better lifting sessions and ultimately higher gains.
By combining structured workouts, progressive overload techniques, and prioritizing recovery, you can effectively incorporate the bench press into your fitness routine and maximize your muscle-building potential.
The Role of Nutrition in Muscle Development
Nutrition plays a pivotal role in muscle development, especially for individuals engaging in strength training, such as bench pressing. Proper dietary habits provide the body with the necessary building blocks to repair and grow muscle tissue after strenuous workouts. The right combination of macronutrients and micronutrients not only supports muscle hypertrophy but also enhances overall performance, recovery, and health. Essential nutrients work synergistically to facilitate the recovery and growth of muscle following the stress of lifting weights.
Proper intake of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats is crucial, as well as vitamins and minerals that contribute to metabolic processes.
Essential Nutrients for Muscle Recovery and Growth, What muscles does benching workout
To effectively support muscle development, it is vital to focus on the following essential nutrients. Each plays a unique role in recovery and growth following bench pressing.
- Protein: Essential for muscle repair and growth, protein provides the amino acids necessary for rebuilding muscle fibers that are damaged during workouts. Aim for lean sources like chicken, fish, eggs, and plant-based options like legumes and quinoa.
- Carbohydrates: They serve as a primary energy source for workouts and help replenish glycogen stores depleted during intense training sessions. Complex carbohydrates such as brown rice, oats, and whole-grain pasta are ideal.
- Healthy Fats: Important for hormone production, including testosterone, which plays a role in muscle growth. Sources include avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Micronutrients like vitamin D, calcium, magnesium, and zinc support various metabolic functions crucial for muscle recovery and overall health. Leafy greens, dairy products, and nuts are great sources.
Hydration is another critical component in the muscle development equation. Staying adequately hydrated aids in nutrient transport, temperature regulation, and muscle function. Dehydration can lead to decreased performance and hinder recovery.
Hydration Strategies for Strength Training
In order to maximize performance and recovery, it’s important to implement effective hydration strategies. Proper hydration before, during, and after workouts can significantly impact strength training outcomes.
- Pre-workout Hydration: Aim to drink at least 16-20 ounces of water two hours before exercising to ensure optimal hydration levels.
- During Workout Hydration: Consume 7-10 ounces of water every 10-20 minutes during workouts, especially in longer sessions or in hot conditions.
- Post-workout Hydration: Rehydrate with 16-24 ounces of water for every pound lost during exercise. Including electrolytes can assist in recovery.
“Adequate hydration not only supports physical performance but also enhances cognitive function, ensuring you remain focused during your training.”
Incorporating a well-rounded nutritional approach, including essential nutrients and hydration strategies, is fundamental for anyone looking to progress in strength training and muscle development. The right dietary choices can enhance the effectiveness of bench pressing and other strength-training exercises, ensuring a solid foundation for growth and recovery.
Final Summary: What Muscles Does Benching Workout
In conclusion, mastering the bench press is about more than just adding weights to the bar; it’s about harnessing the power of your muscles effectively and safely. By focusing on the primary and secondary muscles involved, learning proper techniques, and incorporating variations into your workouts, you set the stage for impressive gains. Remember, it’s not just about lifting; it’s about lifting smart and fueling your body for optimal performance.
So grab that bar and get ready to unleash your full potential!
FAQ Guide
What is the primary muscle worked in the bench press?
The primary muscle worked in the bench press is the pectoralis major, which plays a crucial role in pushing movements.
Can bench pressing help with muscle growth?
Yes, bench pressing is highly effective for muscle growth, especially in the upper body, when performed with proper technique and progressive overload.
How often should I bench press for optimal results?
For best results, aim to bench press 1-3 times per week, allowing adequate recovery time between sessions.
Are there any safety tips for bench pressing?
Always use a spotter, maintain proper form, and start with lighter weights to avoid injury.
What equipment do I need for bench pressing?
A flat bench and a barbell or dumbbells are essential for performing the bench press effectively.




