What is a proxy in finance? A proxy, in the financial world, is a person or entity authorized to act on behalf of another. This representation plays a crucial role in various financial activities, from voting on corporate matters to hedging risk in derivatives markets. Understanding the intricacies of proxies is key to navigating the complexities of modern finance.
Proxies are used extensively in corporate governance, enabling shareholders to cast votes on company decisions without physically attending meetings. They also feature prominently in hedging strategies, allowing investors to mitigate risk in derivative instruments. Different types of proxies exist, each with specific characteristics and applications.
Introduction to Proxies in Finance
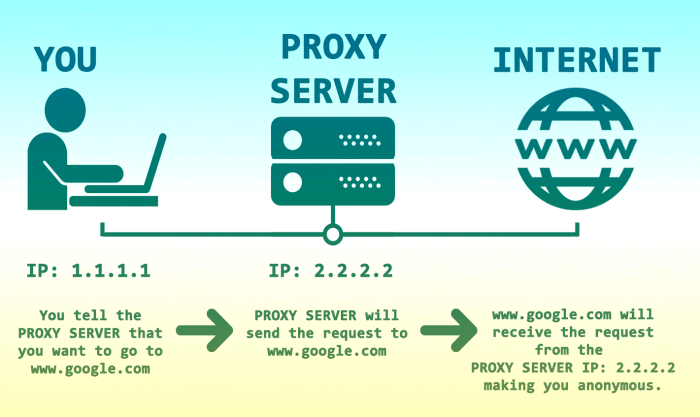
Yo, finance fam! Ever wonder how your investments get managed when you’re not directly involved? That’s where proxies come in. Think of them as your digital stand-ins, authorized to make decisions on your behalf in the financial world. They’re pretty crucial for a smooth flow of things, especially in big, complicated situations.Proxies are essentially representatives in finance.
They act on behalf of someone else, giving them a voice and the power to take action in financial markets or company affairs. This is super important for things like voting on corporate matters, managing large portfolios, or even participating in complex transactions where direct involvement isn’t possible or practical. Basically, proxies make things easier and more efficient for everyone.
Different Types of Financial Proxies
Financial proxies come in various forms, each tailored for specific situations. Understanding the types helps you grasp how they work in different scenarios.
- Voting Proxies: These are common in corporate settings. They allow shareholders to grant someone else the right to vote on their behalf in shareholder meetings. This is especially useful for shareholders who can’t attend meetings personally or want a more experienced party to make the decisions.
- Trading Proxies: These proxies allow an investor to authorize another party to execute trades on their behalf. This is handy for managing large portfolios or when the investor wants to delegate the trading decisions to someone with expertise.
- Investment Proxies: These proxies are often used in situations where an investor wants to entrust their funds to a financial advisor or manager. The advisor then acts as a proxy, making investment decisions on behalf of the investor.
- Legal Proxies: These proxies are used in cases where a person is unable to manage their financial affairs due to illness or other circumstances. A trusted individual can be appointed to act on their behalf. This is crucial for ensuring the well-being of the person involved.
Examples of Proxy Usage, What is a proxy in finance
Proxies are used in numerous financial situations. Let’s take a look at some real-world examples.
- Shareholder Voting: Imagine a major investor who owns a large stake in a company. They might appoint a proxy to vote on behalf of them on issues like mergers, acquisitions, or even board elections. This allows the investor to maintain influence without having to attend the meeting in person.
- Portfolio Management: A retail investor might appoint a financial advisor as their proxy to manage their investments. The advisor can make buying and selling decisions, balancing risk and return based on the investor’s objectives.
- Complex Transactions: In a large merger or acquisition, the management team of one of the companies might use a proxy to manage the transaction’s complexities and represent the company’s interests during the negotiations. It helps keep things organized and streamlined.
Key Characteristics of Different Proxy Types
This table highlights the key differences between various proxy types.
| Proxy Type | Description | Example | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Voting Proxy | Authorizes someone to vote on behalf of a shareholder. | A shareholder delegates voting rights to a proxy firm. | Shareholder meetings, corporate decisions. |
| Trading Proxy | Allows a party to execute trades on behalf of an investor. | A retail investor delegates trading decisions to a brokerage firm. | Portfolio management, high-volume trading. |
| Investment Proxy | Authorizes a financial advisor to manage investments. | An investor appoints a wealth manager to oversee their portfolio. | Investment decisions, diversification strategies. |
| Legal Proxy | Allows a trusted individual to manage financial affairs on behalf of someone unable to do so. | A family member manages finances for a disabled relative. | Protecting financial interests of individuals with limited capacity. |
Proxy Voting and Shareholder Rights
Yo, peeps! So, proxy voting is like a stand-in system for shareholders. Imagine you’re a shareholder with a ton of stock but can’t make it to the annual meeting. Proxy voting lets you give someone else the power to vote on your behalf. It’s super crucial for maintaining shareholder rights and influencing corporate decisions.Proxy voting is a fundamental aspect of corporate governance, enabling shareholders to exert their influence over the company’s direction without physically attending the meeting.
It ensures that shareholders’ voices are heard and considered, even when they cannot attend in person. It’s all about empowering those who own a piece of the company to have a say in how it’s run.
Proxy Voting Process
The proxy voting process typically involves a shareholder granting their voting rights to a designated proxy. This proxy then represents the shareholder’s interests at the corporate meeting. This involves the shareholder signing a proxy form, which details the specific votes they want the proxy to cast. This formal process is crucial for maintaining transparency and accountability in corporate decision-making.
Shareholder Rights with Proxies
Shareholders have a range of rights when using proxies. They can vote on key issues, such as electing directors, approving mergers or acquisitions, and other significant corporate actions. This right allows shareholders to shape the company’s future by influencing the decisions of the board of directors. Essentially, it’s a powerful tool for shareholder engagement.
Significance of Proxy Voting in Corporate Governance
Proxy voting is vital for good corporate governance. It strengthens the link between shareholders and management, allowing shareholders to hold directors accountable for their actions. This system helps ensure that companies are run in a way that benefits all stakeholders, not just the management team.
Potential Conflicts of Interest in Proxy Voting
Conflicts of interest can arise in proxy voting, particularly when the proxy holder has interests that differ from the shareholder’s. For instance, a proxy holder might have financial ties to a particular company or individual that could sway their decisions. Transparency and clear guidelines are needed to mitigate these potential conflicts.
Step-by-Step Guide to Exercising Proxy Voting Rights
- Check your shareholder records to identify the specific procedures and deadlines for proxy voting in your company.
- Obtain the proxy statement, which Artikels the proposals to be voted on and the voting options available.
- Carefully review the information presented in the proxy statement.
- Decide how you want to vote on each proposal. This involves evaluating the proposals and considering the interests of the company and its stakeholders.
- Submit your proxy vote according to the instructions provided by the company, often through an online platform or by mail.
Comparison of Different Proxy Voting Procedures
| Procedure | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Online Voting | Voting is conducted electronically through a secure online platform. | Convenient, accessible, and often faster. | Requires internet access and familiarity with online platforms. |
| Mail Voting | Voting is done by physically submitting a proxy form via mail. | Suitable for shareholders without reliable online access. | Slower than online voting, potential for delays. |
| In-Person Voting | Voting occurs directly at the shareholder meeting. | Allows for direct engagement with company management. | Requires travel and time commitment. |
Proxy Advisors and Their Role
These proxy advisors are like the ultimate taste testers for corporate decisions. They pore over proposals, weigh the pros and cons, and then give shareholders their expert opinion on how to vote. Their recommendations often carry significant weight, shaping the direction of companies and influencing the outcomes of shareholder votes. Imagine them as the savvy consultants, guiding the shareholders to make the right choice.Proxy advisors are crucial intermediaries between corporations and shareholders.
They act as independent experts, analyzing corporate proposals and providing recommendations to shareholders on how to vote. Their insights are valuable, offering an unbiased perspective on potential impacts and ensuring a well-informed decision-making process for shareholders.
Function of Proxy Advisors
Proxy advisors scrutinize corporate proposals, evaluating the potential impacts on shareholders’ interests. Their role extends beyond simply summarizing proposals; they provide in-depth analyses, often incorporating financial modeling and legal considerations. They provide a vital service, ensuring shareholders are equipped with comprehensive information to make informed decisions.
Influence of Proxy Advisors on Corporate Decisions
Proxy advisors’ recommendations often significantly impact corporate decisions. Shareholders, especially institutional investors, often rely heavily on these recommendations when deciding how to vote. This can influence everything from executive compensation to environmental sustainability policies. Their influence can be profound, shaping corporate strategies and fostering a more shareholder-centric approach.
Well-Known Proxy Advisory Firms
Several well-known proxy advisory firms provide invaluable guidance to shareholders. Some prominent examples include Institutional Shareholder Services (ISS) and Glass Lewis. These firms are recognized for their extensive research and analysis capabilities. Their expertise helps investors make informed choices about how to vote.
Methods Used by Proxy Advisors to Analyze Corporate Proposals
Proxy advisors employ various methods to analyze corporate proposals. These methods often involve a combination of qualitative and quantitative factors. They consider financial data, legal frameworks, and broader societal implications. Their analytical approach ensures a thorough evaluation, incorporating different perspectives to arrive at a well-rounded recommendation. For example, ISS might factor in environmental impact alongside financial performance.
Impact of Proxy Advisor Recommendations on Shareholder Votes
Proxy advisor recommendations can substantially influence shareholder votes. When a large institutional investor follows a recommendation, it can significantly sway the outcome of a vote. This influence underscores the importance of proxy advisors in shaping corporate governance. Shareholders often view these recommendations as a crucial part of their decision-making process.
Comparison of Different Approaches by Various Proxy Advisors
Different proxy advisors may adopt slightly different approaches to analyzing corporate proposals. For example, ISS might prioritize environmental and social factors more heavily than Glass Lewis. These differences reflect the diverse perspectives of the advisory firms. Understanding these variations allows shareholders to assess recommendations from different viewpoints.
Proxies in Derivatives and Hedging

Proxies are pretty crucial in the finance world, especially when it comes to derivatives and hedging strategies. Imagine you’re a trader trying to protect yourself from market fluctuations—proxies can be your secret weapon. They allow you to indirectly manage risk, which is super important in today’s volatile markets.
How Proxies Operate in Derivative Instruments
Proxies in derivatives often act as stand-ins for the underlying asset. This is particularly useful when the actual asset is hard to access or track directly. Think of it like a substitute—it mirrors the characteristics of the original asset, like price movements, to provide a way to manage risk. This indirect approach allows traders to gain exposure or reduce risk related to the underlying asset without needing direct ownership.
Use of Proxies in Hedging Strategies
Hedging is all about minimizing risk in your financial positions. Proxies can be employed in various hedging strategies to achieve this. By using a proxy, you’re essentially betting on the correlated behavior of the substitute asset rather than the original. This can significantly reduce your exposure to market volatility.
Risks Associated with Proxy Hedging
While proxies can be great for risk management, they do come with their own set of potential risks. The biggest one is the correlation between the proxy and the actual asset might not be perfect. If the proxy’s performance deviates significantly from the underlying asset, your hedging strategy could backfire, leading to unexpected losses. Another risk is the liquidity of the proxy—if it’s not easily traded, it can be difficult to execute your hedging strategy efficiently.
How Proxies Mitigate Risk in Financial Markets
Proxies play a vital role in mitigating risks in financial markets. They offer an alternative way to manage exposure to certain assets without having to directly hold them. This flexibility is crucial for investors and traders who need to adapt to changing market conditions.
Examples of Proxy Use in Different Derivative Contracts
Proxies are used in various derivative contracts, like futures and options. For example, if you’re hedging your exposure to a specific stock, you might use an exchange-traded fund (ETF) tracking the same sector as a proxy. This allows you to manage risk without owning the underlying stock. In commodity trading, agricultural futures might be hedged with proxies like agricultural ETFs.
Table Contrasting Different Hedging Strategies Using Proxies
| Hedging Strategy | Proxy Used | Risk Mitigation | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Short Selling | Put option on a related stock | Reduces risk of price declines in a portfolio of stocks | A trader shorting stock ABC might use a put option on a stock in the same industry as a proxy. |
| Long Position Hedging | Inverse ETF | Reduces risk of price increases in a portfolio of stocks | An investor holding a stock portfolio might use an inverse ETF to hedge against further price appreciation. |
| Commodity Price Hedging | Agricultural Futures | Reduces risk of commodity price volatility | A farmer growing corn might use agricultural futures to hedge against a potential drop in corn prices. |
Proxies in Financial Reporting and Disclosure
Yo, peeps! Ever wonder how companies, especially the big kahunas, report their financial stuff? It’s not just about the numbers; it’s also about the
- how* and the
- why*. Proxies play a crucial role in this, acting as a link between the shareholders and the company’s actions. Think of it like a translator, ensuring everyone’s on the same page, especially when it comes to crucial decisions.
Proxy Disclosure Requirements
Companies need to be transparent with their financial info, and proxies are a key part of that. Different countries have different rules about what needs to be disclosed regarding proxies. This ensures fairness and allows investors to make informed decisions. Knowing these rules is vital for everyone involved.
- United States: The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) mandates specific disclosures in proxy statements, including details about the company’s activities, compensation for directors, and any potential conflicts of interest. This makes sure everything’s above board, preventing shady dealings.
- Europe: European Union regulations dictate the disclosure requirements for proxies, ensuring a high level of transparency in financial reporting across the continent. Different countries might have their specific nuances, but the overall goal is the same: clear and accessible info for all.
- Asia: Asian jurisdictions, like Singapore and Japan, also have their own sets of regulations regarding proxy disclosures. These rules often align with international best practices but might have specific regional considerations.
Importance of Transparency
Transparency in proxy-related disclosures is paramount. Imagine a situation where a company hides crucial info about a potential acquisition. This lack of transparency can mislead investors and potentially harm the market. Openness and honesty are crucial to maintaining trust.
A proxy in finance, essentially, is a substitute. It’s like a representative, granting someone else the power to act on your behalf. Now, given the recent questions about the legitimacy of United Finance, as discussed on Reddit ( is united finance legit reddit ), understanding proxies becomes even more critical. Ultimately, a proxy allows for delegated decision-making in financial matters, much like entrusting a trusted friend to manage your investments.
Transparency in financial reporting, particularly concerning proxies, is essential for building investor confidence and maintaining market integrity. This helps prevent market manipulation and fosters a fair environment for everyone involved.
Examples of Financial Reporting Standards
Various financial reporting standards incorporate proxies. For instance, International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) and US Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) both emphasize the importance of clear and accurate disclosure related to proxies.
- IFRS: IFRS standards generally require companies to disclose material information about proxies, such as the voting results and any significant shareholder actions.
- GAAP: GAAP standards often highlight the need for accurate and timely disclosure of proxy voting results and the actions taken by the company’s management, directors, or shareholders.
Flowchart of Proxy Disclosure in Financial Reporting
This flowchart Artikels the general process, though specific steps may vary depending on the jurisdiction and the company’s size.
The above flowchart shows the general process of proxy disclosure in financial reporting. It’s crucial for the company to follow these steps accurately and transparently to ensure compliance with regulations and maintain trust with investors.
Challenges and Issues with Proxies in Finance
Bro, proxies in finance can be a real game-changer, but they ain’t without their flaws. Just like any tool, understanding the potential pitfalls is crucial to using them effectively. From limitations in transactions to ethical considerations and potential conflicts, there’s a whole lot to unpack.
Potential Limitations of Using Proxies in Financial Transactions
Using proxies can sometimes limit the direct interaction in financial transactions. For example, a shareholder might not have the same level of control or insight when they’re relying on a proxy to vote on their behalf. This can impact the ability to make informed decisions or negotiate effectively. There’s also the risk of delays or miscommunications, which can impact the speed and efficiency of transactions.
Ethical Considerations Related to Proxies in Finance
Ethical considerations surrounding proxies are super important. Issues like conflicts of interest, especially in proxy voting, are a major concern. Proxy advisors, for instance, might have interests that could influence their recommendations, potentially affecting the decisions of the shareholders they’re supposed to represent. Ensuring transparency and accountability is key to maintaining trust and avoiding ethical breaches.
Potential for Conflicts of Interest in Proxy Voting
Conflicts of interest in proxy voting are a significant concern. For example, a proxy advisor might have financial ties to a particular company or a competing entity, which could lead to biased recommendations. This bias could influence the voting outcomes, potentially leading to decisions that don’t truly reflect the best interests of the shareholders. Maintaining impartiality and independence is paramount to avoiding these conflicts.
Impact of Regulatory Changes on Proxy Practices
Regulatory changes significantly impact proxy practices. New regulations can alter the way proxies are used, from the information required for proxy statements to the processes involved in proxy voting. Changes in regulations can also affect the role and responsibilities of proxy advisors. Staying updated with these changes is crucial for compliance and effective use of proxies.
Comparison of Different Legal Frameworks Surrounding Proxies in Various Jurisdictions
Different countries have different legal frameworks governing proxies. For instance, some jurisdictions might have stricter regulations regarding the disclosure of information in proxy statements, or the process of proxy voting. Comparing these frameworks is essential for understanding the nuances and implications of proxy practices in different markets. Knowing these differences can help investors navigate complex legal landscapes and make informed decisions.
Future Trends in Proxies in Finance

The world of finance is constantly evolving, and proxies are no exception. From digital voting to AI-powered advisory services, the future of proxies is looking pretty tech-savvy. We’re gonna dive into how these changes will impact everything from shareholder rights to financial reporting.
Future Direction of Proxy Usage
Proxy usage is expected to become even more prevalent as investors seek more direct control over their investments. The rise of online platforms and digital voting systems is streamlining the process, making it easier for retail investors to participate. This accessibility, combined with growing awareness of shareholder rights, will likely boost proxy activity in the coming years. Think about how online platforms like Robinhood have empowered everyday investors – a similar shift is expected for proxy voting.
Impact of Technological Advancements
Tech is rapidly transforming proxy procedures. Blockchain technology could revolutionize voting security, ensuring transparency and tamper-proof records. AI-powered tools can analyze vast amounts of data to identify potential conflicts of interest and suggest optimal voting strategies, potentially increasing the effectiveness of proxy voting. Imagine algorithms sifting through reams of corporate info to predict how a company will perform – and suggesting how to vote accordingly!
Emerging Trends in Proxy Advisory Services
Proxy advisory firms are evolving to meet the needs of a more sophisticated investor base. Expect to see more tailored advice, focusing on specific ESG (environmental, social, and governance) factors. Firms are also expected to offer more integrated services, combining proxy analysis with investment research and portfolio management strategies. This means more holistic advice, going beyond just voting suggestions.
Effects of Evolving Regulations
Regulatory changes are shaping the proxy landscape. More stringent disclosure requirements will likely force companies to be more transparent about their operations and governance. This could lead to greater scrutiny of proxy voting decisions, and might affect how investors weigh proxy votes in their investment choices. Think about increased transparency around environmental impact, for instance.
New Applications of Proxies in Finance
Proxies are likely to find new applications in areas like derivative trading and hedging strategies. Investors could use proxies to create more sophisticated hedging strategies and better manage risks. This could lead to more efficient capital markets and better risk management.
Table Predicting Future Trends in Proxy Usage
| Trend | Description | Potential Impact | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Increased Digital Voting | Proxy voting will shift to more online platforms, making it easier for investors to participate | Greater accessibility and efficiency for retail investors. | A shareholder can cast a vote from their phone. |
| AI-Powered Advisory Services | AI will analyze data and suggest optimal voting strategies | More informed and strategic voting decisions, potentially leading to better investment outcomes. | An algorithm suggests voting against a company due to potential ethical concerns. |
| Focus on ESG Factors | Proxy advisory firms will prioritize environmental, social, and governance factors. | Investors will have more holistic information to make decisions, leading to better corporate governance. | A firm suggests voting against a company with poor environmental records. |
| Enhanced Transparency | Increased disclosure requirements force companies to be transparent. | Greater scrutiny of proxy voting decisions, impacting investor confidence and market efficiency. | A company must disclose its environmental impact reports, making it transparent to investors. |
Closing Notes
In conclusion, proxies are fundamental to modern finance. They empower shareholders, facilitate risk management, and shape corporate decisions. While proxies offer significant benefits, potential conflicts of interest and limitations must be considered. The future of proxies in finance hinges on technological advancements, evolving regulations, and emerging applications. Navigating this complex landscape requires a thorough understanding of the various types of proxies, their specific functions, and the potential challenges they present.
Quick FAQs: What Is A Proxy In Finance
What are the different types of financial proxies?
Financial proxies encompass various forms, including voting proxies for shareholders, proxies used in hedging strategies with derivative instruments, and proxies employed in financial reporting for disclosure purposes.
How do proxy advisors influence corporate decisions?
Proxy advisors analyze corporate proposals and provide recommendations to shareholders, which can significantly impact shareholder votes and, consequently, corporate decisions.
What are some common conflicts of interest associated with proxy voting?
Conflicts of interest can arise when proxy voting is influenced by factors beyond the best interests of the shareholders, such as personal gain or pressures from external parties.
How do proxies mitigate risk in financial markets?
Proxies can be employed in hedging strategies to reduce the exposure to market fluctuations and minimize potential losses.





