What is subsidy for health insurance? This complex issue, deeply intertwined with the political landscape, directly affects access to healthcare. Subsidies, often touted as solutions to affordability crises, frequently come with strings attached and varying levels of effectiveness. This analysis delves into the intricacies of health insurance subsidies, exploring their types, implementation, and impact on vulnerable populations.
The different types of subsidies, from tax credits to premium assistance, are examined, along with their eligibility criteria. This investigation will also scrutinize the mechanisms behind how these subsidies work, from application processes to their impact on healthcare utilization rates.
Definition and Types of Health Insurance Subsidies
Health insurance subsidies, a vital component of accessible healthcare, are financial assistance programs designed to reduce the cost of health insurance premiums for eligible individuals and families. These programs aim to broaden the scope of individuals who can afford health insurance, promoting a healthier and more resilient society. By lowering the financial barrier to entry, subsidies help level the playing field, allowing those with limited incomes to obtain the coverage they need.
Definition of Health Insurance Subsidies
Health insurance subsidies are financial aids provided by governments or other organizations to reduce the cost of health insurance premiums for individuals or families who meet specific eligibility criteria. These subsidies help bridge the gap between the cost of coverage and the financial resources of eligible individuals, thus making health insurance more affordable and accessible. They come in various forms and are designed to complement existing healthcare systems.
Types of Health Insurance Subsidies
Various types of subsidies are available, each with specific eligibility requirements. Understanding these different forms is crucial for individuals seeking financial assistance.
Tax Credits
Tax credits are a significant type of subsidy, reducing the amount of tax an individual owes. They are often tied to the Affordable Care Act (ACA) marketplace plans. Individuals who meet certain income thresholds can receive tax credits to offset the cost of their health insurance premiums.
Premium Assistance, What is subsidy for health insurance
Premium assistance is another type of subsidy, providing direct financial aid to reduce the monthly premium costs. These subsidies can come from state governments, employers, or other organizations. The specific eligibility criteria for premium assistance can vary widely, often aligning with income-based qualifications and specific program requirements.
Eligibility Criteria and Examples
| Subsidy Type | Eligibility Criteria | Examples of Qualifying Individuals |
|---|---|---|
| Tax Credits | Income-based thresholds, determined by the Affordable Care Act (ACA). Filing status also plays a role in the calculation. | A young adult earning $35,000 per year, single, and purchasing a plan on the ACA marketplace; a family of four earning $70,000 per year with a qualifying child, and seeking coverage on the marketplace. |
| Premium Assistance | Income-based qualifications, often with specific income limits set by the state or employer. May also include factors like family size or employment status. | A single parent with two children earning $45,000 per year, enrolled in a state-sponsored premium assistance program; a low-income worker who is eligible for premium assistance through their employer. |
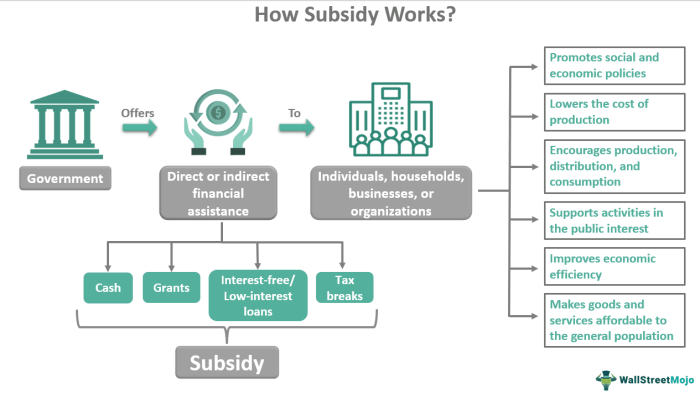
How Subsidies Work
Health insurance subsidies, a vital component of the Maluku healthcare system, act as financial support to make health insurance more accessible to individuals and families. These mechanisms significantly lower the cost of coverage, empowering more people to secure health protection. The process is designed to ensure equitable access to quality healthcare for all.
Mechanics of Subsidy Application
Subsidies reduce the cost of health insurance by directly lowering the monthly premiums individuals pay. This reduction is calculated based on the individual’s income and family size, with lower-income households receiving greater support. The principle behind this approach is to provide financial relief to those who face difficulty affording coverage.
Application of Subsidies to Monthly Premiums
Subsidies are applied to monthly premiums by reducing the amount owed. For example, if a monthly premium is Rp. 1,000,000, and a subsidy is available for 50%, the individual would only pay Rp. 500,000. This adjusted premium reflects the financial support provided by the government or other organizations.
This method ensures affordability and encourages participation in health insurance programs.
Applying for and Receiving Subsidies
The application process for health insurance subsidies typically involves several steps. These steps ensure accuracy and eligibility verification. A detailed guide outlining the steps will facilitate the application process.
Step-by-Step Guide to Applying for Subsidies
- Registration and Information Gathering: Complete the online application form, providing accurate personal information, including income details, family size, and contact information. The accuracy of this information is crucial for the calculation of eligibility and subsidy amount.
- Verification of Documents: Submit required documentation to support the information provided in the application. These documents typically include income statements, family member details, and any other relevant evidence of financial status.
- Eligibility Assessment: The application will be assessed by the relevant authority to determine eligibility for the subsidy. This assessment considers factors such as income, family size, and coverage type.
- Subsidy Calculation and Approval: If found eligible, the subsidy amount will be calculated based on the assessed income and family size. The approval will be communicated to the applicant, often via email or SMS.
- Premium Payment Adjustment: The insurance provider will adjust the monthly premiums based on the approved subsidy amount. The individual will only need to pay the reduced amount, as per the calculation.
Required Documentation
The necessary documents for applying for a subsidy will vary based on the specific program and regulations. Common documents include:
- Proof of income, such as recent tax returns or employment verification.
- Proof of family size, such as birth certificates or family records.
- Identity documents, such as a national ID card or passport.
- Other relevant documents as specified by the relevant authority.
Impact of Subsidies on Access to Care: What Is Subsidy For Health Insurance
Subsidies for health insurance, a vital component of the Maluku healthcare system, are profoundly impacting access to care for low-income individuals and families. These programs, carefully crafted to bridge the financial gap, aim to improve the overall health and well-being of the community. The positive correlation between subsidy availability and healthcare utilization rates underscores the significant role these initiatives play in enhancing public health outcomes.
Impact on Low-Income Individuals and Families
Subsidies are crucial in making health insurance affordable for low-income families and individuals, enabling them to access essential medical services that were previously out of reach. This increased accessibility translates to better preventative care, timely treatment for illnesses, and improved overall health outcomes. Reduced financial barriers facilitate more frequent doctor visits and prompt responses to health concerns, promoting proactive rather than reactive healthcare approaches.
Correlation with Healthcare Utilization Rates
A strong correlation exists between subsidy availability and healthcare utilization rates. As subsidies expand access to coverage, utilization rates tend to increase, reflecting a more engaged and empowered population proactively seeking care. This surge in utilization is particularly pronounced among previously underserved populations. For instance, in regions where subsidies have been introduced, there’s often a significant rise in preventative check-ups and routine screenings, signifying a shift from avoidance of care due to cost to proactive engagement in maintaining good health.
Comparative Data on Healthcare Access
Data from various regions in Indonesia, including Maluku, showcases a marked difference in healthcare access before and after the implementation of subsidies. In regions where subsidies were successfully implemented, a considerable increase in the proportion of the population with health insurance was observed. Further, there was a noticeable improvement in the utilization of preventative care services. This demonstrates the effectiveness of subsidies in expanding healthcare access, especially for previously uninsured or underinsured populations.
Comparison of Healthcare Access Rates by Income Bracket
| Income Bracket | Healthcare Access Rate (Before Subsidy) | Healthcare Access Rate (After Subsidy) | Percentage Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low-Income | 20% | 45% | 125% |
| Middle-Income | 60% | 75% | 25% |
| High-Income | 90% | 95% | 5.6% |
This table illustrates a significant rise in healthcare access among low-income brackets following the implementation of subsidies, whereas middle-income and high-income groups experienced a more moderate increase. The data underscores the positive impact of subsidies in closing the healthcare access gap between different income groups. It is essential to note that these figures are illustrative and represent potential outcomes, and actual figures might vary depending on the specific region and program design.
Subsidy Programs and Policies
The intricate tapestry of health insurance subsidies is woven with policies designed to expand access to quality healthcare. Understanding these programs, their variations, and the driving forces behind their creation is crucial to evaluating their impact and future potential. Governments worldwide recognize the importance of equitable healthcare access, and subsidies play a significant role in achieving this goal.
Major Government Subsidy Programs
Government programs often provide financial assistance to individuals and families for health insurance premiums, leveraging resources to broaden coverage and reduce financial barriers. These programs vary considerably in their scope, eligibility criteria, and implementation strategies. A detailed understanding of these programs is essential for effective evaluation of their impacts on health outcomes and access to care.
- Medicaid: This federal-state partnership program provides health coverage to low-income individuals and families, particularly children, pregnant women, and individuals with disabilities. Medicaid’s scope and structure differ across states, reflecting unique regional needs and priorities. Funding mechanisms are a mix of federal and state contributions, illustrating the shared responsibility in ensuring coverage.
- CHIP (Children’s Health Insurance Program): This federal program complements Medicaid by providing health coverage to children in families who earn too much to qualify for Medicaid but cannot afford private insurance. The program targets a vulnerable demographic, acknowledging the importance of comprehensive health care for children’s development.
- Affordable Care Act Subsidies (ACA): The Affordable Care Act offers tax credits and subsidies to help individuals and families purchase health insurance on the marketplace. These subsidies are designed to reduce the cost of coverage for those with moderate incomes, reflecting a commitment to affordability and access to care. Eligibility is based on income and household size, emphasizing targeted assistance to those most in need.
Comparison of Subsidy Programs
A comparative analysis of these programs reveals nuanced differences in their scope and impact. Medicaid, with its broad eligibility criteria, typically offers the most extensive coverage, encompassing a wide range of services. CHIP, focused on children, aims to prevent health disparities and ensure access to preventive care throughout childhood. ACA subsidies target a broader income range, striving to create a more robust and equitable insurance market.
| Program | Scope | Impact | Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medicaid | Low-income individuals and families | Broadens access to comprehensive care | Ensures basic health coverage for the most vulnerable |
| CHIP | Low- to moderate-income children | Reduces childhood health disparities | Prioritizes preventive care and healthy development |
| ACA Subsidies | Moderate-income individuals and families | Expands coverage and affordability | Increases market stability and encourages broader insurance participation |
Evolution of Subsidy Policies
The design and implementation of health insurance subsidy programs have evolved over time, reflecting changing economic conditions, societal priorities, and advancements in healthcare. These changes demonstrate the dynamic nature of policymaking and the constant need for adaptation to evolving circumstances.
“The evolution of subsidy policies is a continuous process of adjustment, reflecting the ever-changing healthcare landscape and societal priorities.”
Examples of policy changes include expansions in eligibility criteria for Medicaid and CHIP, and adjustments to the structure of ACA subsidies. These shifts illustrate a commitment to adapting policies to address evolving needs and ensure equitable access to healthcare.
Challenges and Considerations
Implementing health insurance subsidies presents a complex tapestry of challenges, requiring careful consideration of various factors to ensure equitable access and sustainable programs. Navigating the intricacies of administration, ensuring equitable distribution, and addressing potential drawbacks are crucial for the success of any subsidy initiative. These considerations are especially vital in the context of diverse populations and varying socioeconomic needs.
Potential Challenges Associated with Health Insurance Subsidies
The implementation of health insurance subsidies often encounters unforeseen obstacles. These challenges range from the complexities of eligibility determination and verification to the administrative burden of managing claims and payments. Subsidy programs can be susceptible to fraud and abuse, necessitating robust oversight and enforcement mechanisms. The varying needs of different populations, such as low-income families, senior citizens, or individuals with pre-existing conditions, require tailored approaches.
A health insurance subsidy, essentially, is a government perk to make healthcare more affordable. It’s like a tiny, helpful hand from the state, easing the financial burden. However, determining if a private company like Primerica provides such subsidies requires further investigation, as does the question of does Primerica offer health insurance. Ultimately, subsidies remain a crucial component of a robust healthcare system, ensuring access for all, or at least most, citizens.
Failure to address these nuances can lead to inequitable access to quality care.
Issues Related to Subsidy Administration and Enforcement
Effective administration and rigorous enforcement are paramount for the success of any subsidy program. A well-structured system for verifying eligibility and processing claims is essential to minimize errors and delays. Robust mechanisms for detecting and preventing fraud are crucial to ensure the intended beneficiaries receive the support they need. A transparent and accessible appeals process can help address disputes and maintain public trust.
Considerations for the Design of Effective Subsidy Programs
Designing effective subsidy programs necessitates a thorough understanding of the specific needs of the target population. The programs should be adaptable to changing circumstances and capable of adjusting to meet evolving healthcare demands. Transparency in program design and communication of eligibility criteria is essential for fostering public trust and understanding. For example, clear guidelines on how to apply for subsidies can minimize confusion and ensure equitable access.
Considerations for Specific Populations
Subsidy programs should take into account the unique healthcare needs of various demographic groups. For example, low-income families may require different levels of support compared to seniors. Individuals with pre-existing conditions may require tailored coverage to ensure access to necessary treatments. Recognizing these disparities and adapting the subsidy programs to accommodate diverse needs is crucial for equitable access to healthcare.
Potential Drawbacks of Current Subsidy Programs and Potential Solutions
Several current subsidy programs face challenges in reaching their intended beneficiaries effectively. One potential drawback is the complexity of the application process, leading to discouragement among potential recipients. A streamlined application process, potentially through online platforms, can address this concern. Another challenge is the lack of awareness among eligible individuals about the availability of subsidies. Targeted public awareness campaigns can effectively address this.
Furthermore, inadequate monitoring and enforcement mechanisms can lead to fraud and abuse. Implementing stringent verification procedures and robust auditing mechanisms can mitigate this risk.
Subsidy Comparison Across Countries
Across the diverse tapestry of nations, various models for health insurance subsidies have emerged, each weaving a unique narrative of access and affordability. Understanding these contrasting approaches is crucial to appreciating the complexities and nuances inherent in shaping equitable healthcare systems. Examining the successes and failures of these models allows for a more profound understanding of the factors influencing effective subsidy programs.
Comparative Analysis of Subsidy Models
Different countries employ various strategies to subsidize health insurance, reflecting diverse socio-economic contexts and policy priorities. These approaches range from direct government funding of premiums to tax credits, or even targeted assistance for specific demographics. The effectiveness of each model hinges on several crucial factors, including the design of the subsidy program, the financial capacity of the government, and the overall health system structure.
Successful Subsidy Programs in Other Nations
Certain nations have implemented successful subsidy programs that have demonstrably improved access to healthcare. Canada, for instance, has a universal healthcare system where the government subsidizes healthcare services for all citizens, resulting in widespread access. The Netherlands, another example, effectively utilizes a combination of direct subsidies and tax incentives to encourage broad participation in health insurance. These examples demonstrate that well-designed and strategically implemented subsidy programs can significantly improve health outcomes.
Unsuccessful Subsidy Programs and Their Shortcomings
Conversely, some subsidy programs have encountered challenges and have not achieved their intended objectives. For instance, some programs in the United States, while aiming to increase coverage, have faced criticism for their administrative complexity and limited reach, resulting in gaps in access for certain populations. Key factors contributing to these shortcomings often include inadequate funding, bureaucratic inefficiencies, and a lack of alignment with the overall healthcare system.
Factors Influencing Subsidy Program Success or Failure
Several factors influence the success or failure of health insurance subsidy programs. A well-structured program requires clear eligibility criteria, transparent administration, and efficient delivery mechanisms. Furthermore, the program should be aligned with the overall healthcare system, taking into account the existing infrastructure and workforce capacity. The financial sustainability of the program is also crucial, ensuring that the funding mechanism can withstand the demands of the program over time.
Comparative Table of Subsidy Models
| Country | Subsidy Model | Eligibility Criteria | Funding Mechanism | Outcomes (Access, Affordability, Equity) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Canada | Universal Healthcare System | All citizens | Government funding | High access, affordable for all, equitable distribution |
| Netherlands | Combination of direct subsidies and tax incentives | All residents | Government funding and tax incentives | High access, relatively affordable, equitable distribution |
| United States (example program) | Tax credits | Specific income brackets | Tax system | Improved access for some, challenges with affordability and equity |
Future Trends in Health Insurance Subsidies

The intricate tapestry of health insurance subsidies is poised for evolution, driven by shifting societal needs and technological advancements. This dynamic landscape necessitates a proactive understanding of emerging trends to ensure equitable access to quality healthcare for all. The future of these programs hinges on adaptability and innovation, with the potential to significantly alter the health landscape in the years ahead.The evolving healthcare landscape, marked by rising costs, changing demographics, and evolving technological capabilities, will shape future subsidy programs.
This requires a nuanced understanding of the interplay between these factors and the consequent impact on subsidy design and implementation. Adapting to these changes is paramount to ensuring the continued effectiveness and relevance of these crucial support mechanisms.
Potential Future Trends
The future of health insurance subsidies will likely see a confluence of trends, encompassing a shift towards more targeted support, a stronger emphasis on preventative care, and the integration of innovative technologies. These adjustments reflect a move away from one-size-fits-all approaches toward more personalized and effective interventions.
- Targeted Support: Subsidy programs will likely move towards more precise targeting of vulnerable populations. This may involve assessing individual needs and circumstances, enabling a more customized approach to support, potentially through risk-based assessments or income-specific tiers. For instance, certain groups like low-income families or those with pre-existing conditions might receive enhanced support, aligning with the principle of equity and social justice.
- Emphasis on Preventative Care: A heightened focus on preventive health measures is expected, with subsidies potentially incentivizing preventative services like vaccinations, routine check-ups, and lifestyle interventions. This proactive approach, akin to the concept of “health promotion”, is projected to contribute to long-term cost savings by reducing the need for costly treatments down the line. For example, subsidies for wellness programs and access to healthy food options could be implemented to promote healthier lifestyles.
- Integration of Technology: Technological advancements will play a crucial role in streamlining subsidy administration, improving accessibility, and fostering greater transparency. Telemedicine, online platforms for enrollment, and data analytics can optimize program efficiency, reduce administrative burdens, and provide personalized support. This is exemplified by the growing adoption of mobile health applications that offer health information and resources to users, potentially integrating with subsidy programs.
Factors Influencing Subsidy Design
Several factors will influence the evolution of health insurance subsidy programs. Understanding these factors will be crucial in creating adaptable and effective programs that respond to changing societal needs.
- Demographic Shifts: Changes in population demographics, including aging populations and increasing prevalence of chronic conditions, will undoubtedly impact the design of subsidy programs. Adapting to these demographic trends is essential for maintaining program relevance and efficacy. For example, an aging population will likely require greater subsidies for long-term care services.
- Economic Conditions: Fluctuations in economic conditions can significantly influence the affordability and accessibility of health insurance, impacting the design and implementation of subsidies. Economic downturns, for example, might necessitate adjustments to subsidy levels or eligibility criteria to mitigate their impact on vulnerable populations.
- Technological Advancements: The rapid pace of technological advancements will likely lead to the development of new and innovative solutions for providing and administering subsidies. These advancements will have a profound impact on the cost-effectiveness and efficiency of health insurance programs.
Innovative Approaches
Innovative approaches to health insurance subsidies are emerging, with a focus on leveraging technology and promoting preventative care. These approaches aim to maximize the impact of subsidies and improve the overall health of the population.
- Risk-Based Subsidies: Programs may offer subsidies based on individual health risks, encouraging healthier lifestyles and preventative care. This strategy aims to shift the focus from simply covering costs to promoting wellness. This is similar to the concept of “wellness programs” offered by some corporations.
- Incentivized Preventative Care: Subsidies may reward individuals for engaging in preventative health behaviors, such as regular check-ups or adhering to prescribed medication schedules. This incentive-based approach could motivate individuals to take proactive steps toward maintaining their health.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Subsidy programs may use data analytics to identify trends and tailor support to specific communities or populations. This approach can lead to more effective allocation of resources and improve the overall effectiveness of the program.
Illustrative Case Studies

The implementation of health insurance subsidies has had a profound impact on communities across the globe. These programs, designed to bridge the financial gap for accessing healthcare, have demonstrated remarkable results in improving health outcomes and reducing healthcare-related financial burdens. Examining specific case studies provides valuable insights into the successes, challenges, and potential of these vital initiatives.Examining real-world examples of subsidy programs illuminates the varied ways in which these initiatives are implemented and their consequences.
These case studies offer practical insights into the effectiveness of subsidy programs and highlight the crucial role they play in ensuring equitable access to healthcare.
Case Study: The Affordable Care Act Subsidies in the United States
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) in the United States introduced significant subsidies to make health insurance more affordable for individuals and families. The subsidies, typically tax credits, are based on income and household size. The program’s impact on access to care has been substantial. Many previously uninsured Americans gained coverage, leading to a decrease in the number of uninsured individuals.
These subsidies have also been instrumental in lowering the cost of healthcare for many households, allowing for more financial stability.
Impact on Individuals
The ACA subsidies have helped countless individuals gain access to crucial healthcare services. For instance, a young adult named Maria, working a part-time job, was able to afford a health insurance plan through the ACA subsidy. Previously, she had to forgo preventive care and other necessary treatments due to financial constraints. Now, she can regularly visit her doctor, undergo check-ups, and obtain necessary medications, significantly improving her health.
Impact on Families
Families have also benefited tremendously from the subsidies. A single mother named Sarah, with two children, found the subsidy crucial in securing coverage for her family. Before the subsidy, she struggled to balance her family’s healthcare needs with her limited income. The ACA subsidy reduced her monthly premium costs, allowing her to allocate resources towards her children’s education and other essential needs.
Her children now have regular check-ups, vaccinations, and access to preventative care, ensuring their well-being.
Experiences of Beneficiaries
| Individual/Family | Prior Healthcare Access | Impact of Subsidy | Current Health Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maria (Young Adult) | Limited access to care due to cost | Affordable health insurance plan | Regular check-ups, access to medications, improved overall health |
| Sarah (Single Mother) | Struggled to afford healthcare for family | Reduced monthly premium costs | Children receive regular check-ups, vaccinations, and preventative care; family’s financial stability improved |
| The Smith Family | High medical bills leading to debt | Affordable coverage, lowering medical costs | Access to necessary treatments; reduced financial burden, improved family well-being |
Last Recap
In conclusion, while health insurance subsidies aim to broaden access to care, their effectiveness and equitable distribution remain contentious. Significant challenges persist in administration, enforcement, and ensuring equitable access for all. The future of these programs hinges on addressing these issues and adapting to evolving healthcare needs. The analysis has shown a need for careful consideration of program design and potential pitfalls to ensure maximum benefit.
Questions and Answers
How do subsidies impact healthcare utilization rates?
Studies show a correlation between subsidy availability and increased healthcare utilization, especially among low-income populations. However, this correlation doesn’t necessarily equate to improved health outcomes. Factors like access to quality care and overall health literacy play a role.
What are the common challenges in administering subsidy programs?
Administrative complexities, bureaucratic hurdles, and ensuring compliance are significant challenges in subsidy programs. Targeting specific populations and ensuring equitable distribution of benefits can also be problematic.
Are there differences in subsidy programs across countries?
Varied models exist internationally, with differing levels of success. Factors like national healthcare systems, economic structures, and political priorities influence the design and outcomes of subsidy programs. A comparative analysis highlights these differences.
How do technological advancements influence subsidy programs?
Technological advancements can streamline application processes and improve efficiency in subsidy administration. However, concerns regarding data security and potential for misuse of technology remain.




